The application in electronic form is how it is made out. How the "Application" section is drawn up in the thesis (course) work
GOST 2.105-95
Group T52
INTERSTATE STANDARD
Unified system for design documentation
GENERAL REQUIREMENTS FOR TEXT DOCUMENTS
Unified system for design documentation. General requirements for textual documents
ISS 01.110
OKSTU 0002
Date of introduction 1996-07-01
Foreword
1 DEVELOPED by the All-Russian Research Institute of Standardization and Certification in Mechanical Engineering (VNIINMASH) of the State Standard of Russia
INTRODUCED by Gosstandart Russian Federation
2 ADOPTED by the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (Protocol No. 7 dated April 26, 1995)
Voted for adoption:
State name | Name of the national standardization body |
The Republic of Azerbaijan | Azgosstandart |
Republic of Armenia | Armgosstandart |
Republic of Belarus | State Standard of the Republic of Belarus |
Georgia | Gruzstandart |
The Republic of Kazakhstan | Gosstandart of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
Republic of Kyrgyzstan | Kyrgyzstandard |
The Republic of Moldova | Moldovastandart |
the Russian Federation | Gosstandart of Russia |
The Republic of Tajikistan | Tajikstandart |
Turkmenistan | Glavgosluzhba "Turkmenstandartlary" |
The Republic of Uzbekistan | Uzgosstandart |
Ukraine | State Standard of Ukraine |
Amendment No. 1 was adopted by the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification by correspondence (Minutes No. 23 of February 28, 2006)
The national standardization bodies of the following states voted for the adoption of the change: AZ, AM, BY, KZ, KG, MD, RU, TJ, TM, UZ, UA [alpha-2 codes according to IEC (ISO 3166) 004]
3 By the Resolution of the Committee of the Russian Federation for Standardization, Metrology and Certification of August 8, 1995 N 426, the interstate standard GOST 2.105-95 was put into effect as a state standard of the Russian Federation from July 1, 1996.
4 REPLACE GOST 2.105-79, GOST 2.906-71
5 EDITION (April 2011) with Amendment No. 1, approved in June 2006 (IUS 9-2006), Amendment (IUS 12-2001)
Amendment published in IUS N 2, 2012
Corrected by the manufacturer of the database
1 area of use
1 area of use
This International Standard specifies general requirements for the implementation of text documents for mechanical engineering, instrument making and construction products.
2 Normative references
Throughout this standard, references are made to the following standards:
GOST 2.004-88 Unified system for design documentation. General requirements to the execution of design and technological documents on printing and graphic devices for computer output
GOST 2.104-2006 Unified system for design documentation. Basic inscriptions
GOST 2.106-96 Unified system for design documentation. Text documents
GOST 2.109-73 Unified system for design documentation. Basic requirements for drawings
GOST 2.301-68 Unified system for design documentation. Formats
GOST 2.304-81 Unified system for design documentation. Drawing fonts
GOST 2.316-2008 Unified system for design documentation. Rules for applying inscriptions, technical requirements and tables on graphic documents. General Provisions
GOST 2.321-84 Unified system for design documentation. Letter designations
GOST 2.503-90 Unified system for design documentation. Change rules
GOST 6.38-90 * Unified documentation systems. System of organizational and administrative documentation. Requirements for paperwork
_______________
* Canceled without replacement on the territory of the Russian Federation.
GOST 7.32-2001 System of standards for information, librarianship and publishing. Research report. Structure and design rules
GOST 8.417-2002 State system ensuring the uniformity of measurements. Units of quantities
GOST 13.1.002-2003 Reprography. Micrography. Microfilm documents. General requirements and standards
GOST 21.101-97 * System of design documentation for construction. Basic requirements for working documentation
________________
* On the territory of the Russian Federation, GOST R 21.1101-2009 is in force.
GOST 14236-81 Polymer films. Tensile test method
3 General
3.1 Text documents are divided into documents containing mainly continuous text (specifications, passports, calculations, explanatory notes, instructions, etc.), and documents containing text broken down into columns (specifications, statements, tables, etc.) .P.).
Text documents are performed in paper form and (or) in the form of an electronic document (DE).
It is allowed to use abbreviations of words in accordance with GOST 2.316 in text documents containing text divided into columns.
(Modified edition, Amendment N 1).
3.2 Text documents are performed on the forms established by the relevant standards of the Unified System for Design Documentation (ESKD) and the System for Design Documentation for Construction (SPDS).
Requirements specific to certain types of text documents (for example, operational documents) are given in the relevant standards.
3.3 Originals of text documents are performed in one of the following ways:
- typewritten, while the requirements of GOST 13.1.002 should be followed. The typewriter font must be clear, at least 2.5 mm high, the tape is only black (bold);
- handwritten - drawing type in accordance with GOST 2.304 with letters and numbers at least 2.5 mm high. Numbers and letters must be written clearly in black ink;
- using printing and graphic computer output devices (GOST 2.004);
3.4 Copies of text documents are performed in one of the following ways:
- typographic - in accordance with the requirements for publications produced by typographic method;
- by photocopying - it is recommended to reproduce by means of double-sided copying;
- blueprint;
- microfilming;
- on electronic data carriers.
3.3, 3.4 (Modified edition, Amendment N 1).
3.5 Entering into text documents made by a typewritten method, individual words, formulas, conventional signs (handwritten method), as well as illustrations should be done in black ink, paste or ink.
3.6 The distance from the form frame to the text boundaries at the beginning and end of the lines is at least 3 mm.
The distance from the top or bottom line of text to the top or bottom frame must be at least 10 mm.
The paragraphs in the text begin with an indent equal to five strokes of the typewriter (15-17 mm).
An example of the execution of a text document is given in Appendix A.
3.7 Typos, misprints and graphic inaccuracies found during the execution of the document may be corrected by erasing or painting over with white paint and applying the corrected text (graphics) in the same place in a typewritten manner or in black ink, paste or ink by hand.
Damage to sheets of text documents, blots and traces of incompletely deleted previous text (graphics) are not allowed.
After making corrections, the document must meet the microfilming requirements established by GOST 13.1.002.
3.8 To place approving and approving signatures to text documents, it is recommended to draw up a cover page and (or) an approval sheet in accordance with section 6 of this standard.
The obligation and peculiarities of the execution of title pages are stipulated in the ESKD and SPDS standards for the rules for the implementation of the relevant documents.
3.9 It is recommended to issue a change registration sheet for text documents in accordance with GOST 2.503 and GOST 21.101.
3.10 The content and details of the DE must comply with the requirements of the ESKD standard.
The structure and composition of the DE details must ensure its circulation within the software (display, modification, printing, accounting and storage in databases, as well as transfer to other automated systems) while observing the regulatory requirements for the execution of text documents.
4 Requirements for text documents containing mainly solid text
4.1 Document construction
4.1.1. The text of the document, if necessary, is divided into sections and subsections.
With a large volume of the document, it is allowed to divide it into parts, and parts, if necessary, into books. Each part and book is completed separately. All parts are given a name and a document designation is assigned. Starting from the second part, a serial number is added to this designation, for example: XXXX.331112.032F0, XXXX.331112.032F01, XXXX.331112.032F02, etc. All books are given a title and assigned a serial number. An example of filling in field 4 of the title page for a book is given in Appendix B.
The sheets of the document are numbered within each part, each part begins on sheets with a main inscription in the form of GOST 2.104 and Form 3 of GOST 21.101.
4.1.2. Sections should have serial numbers within the entire document (parts, books), designated by Arabic numerals without a period and written with paragraph indentation. Subsections should be numbered within each section. A subsection number consists of section and subsection numbers, separated by a dot. A full stop is not put at the end of the subsection number. Sections, like subsections, can consist of one or more items.
4.1.3 If the document does not have subsections, then the numbering of clauses in it should be within each section, and the clause number should consist of the section and clause numbers, separated by a dot. There is no full stop at the end of the item number, for example:
1Types and main dimensions
Numbering of paragraphs in the first section of the document
2Technical requirements
Numbering of paragraphs in the second section of the document
If the document has subsections, then the numbering of clauses should be within the subsection and the clause number should consist of the section, subsection and clause numbers, separated by dots, for example:
3 Test methods
3.1 Apparatus, materials and reagents
Numbering of paragraphs of the first subsection of the third section of the document
3.2 Test preparation
Numbering of clauses in the second subsection of the third section of the document
4.1.4 If a section or subsection consists of one paragraph, it is also numbered.
4.1.5 If the text of the document is subdivided into paragraphs only, they are numbered with serial numbers within the document.
4.1.6 Clauses, if necessary, can be divided into sub-clauses, which must be sequentially numbered within each clause, for example: 4.2.1.1, 4.2.1.2, 4.2.1.3, etc.
4.1.7 Enumerations may be given within clauses or subclauses.
Each item of the enumeration should be preceded by a hyphen or, if necessary, a link in the text of the document to one of the enumerations, a lowercase letter of the Russian or Latin alphabets, followed by a parenthesis. For further detailing of the enumerations, it is necessary to use Arabic numerals, after which a parenthesis is placed, and the entry is made with paragraph indentation as shown in the example.
Example.
a) ______________
b) ______________
1) ______________
2) ______________
v) ______________
(Modified edition, Amendment N 1).
4.1.8 Each item, sub-item and listing is recorded with paragraph indentation.
4.1.9 Sections, subsections must have headings. Paragraphs, as a rule, do not have headings.
Headings should clearly and concisely reflect the content of sections, subsections.
Headings should be printed with capital letter without a period at the end, without underlining. Word hyphenation in titles is not allowed. If the title consists of two sentences, separate them with a period.
The distance between the heading and the text when performing a document in a typewritten way should be equal to 3, 4 intervals, when performing in a handwritten way - 15 mm. The distance between the headings of a section and subsection is 2 spacing, when executed in a handwritten way - 8 mm. When executing text documents in an automated way, it is allowed to use distances close to the specified intervals.
(Modified edition, Amendment N 1).
4.1.10 Each section of a text document is recommended to start with a new sheet (page).
4.1.11 In a document (part, book) of a large volume, on the first (title) sheet and, if necessary, on subsequent sheets, place the content, including the numbers and names of sections and subsections, indicating the numbers of sheets (pages).
If the document is divided into parts (books), then at the end of the content of the first part (books), the designation and name (if any) of the remaining parts (books) are listed. The content is included in the total number of sheets of this document (parts, books).
The word "Content" is written in the form of a heading (symmetrically to the text) with a capital letter. The titles included in the content write lowercase letters starting with an uppercase letter.
4.1.12 At the end of the text document, before the change registration sheet, it is allowed to provide a list of references that was used in its preparation. Execution of the list and references to it in the text - in accordance with GOST 7.32. References are included in the content of the document.
4.1.13. The page numbering of the document and the annexes included in this document must be continuous. Instead of continuous page numbering, it is allowed to use page numbering within each section of the document as follows:
3 15
section page
4.2 Text of documents
4.2.1 Full name of the product on title page, in the title block and at the first mention in the text of the document must be the same with its name in the main design document.
In the following text, the word order in the name should be direct, i.e. in the first place should be the definition (adjective), and then the product name (noun); in this case, it is allowed to use the abbreviated name of the product.
The names given in the text of the document and in the illustrations must be the same.
4.2.2 The text of the document should be short, clear and not allow for different interpretations.
When stating mandatory requirements in the text, the words “should”, “should”, “necessary”, “it is required that”, “only allowed”, “not allowed”, “prohibited”, “should not” should be used. When stating other provisions, the words “may be”, “as a rule”, “if necessary”, “may be”, “in case”, etc. should be used.
In this case, it is allowed to use a narrative form of presentation of the text of the document, for example, "apply", "indicate", etc.
The documents should use scientific and technical terms, designations and definitions established by the relevant standards, and in their absence - generally accepted in the scientific and technical literature.
If a specific terminology is adopted in a document, then at the end of it (before the list of references) there should be a list of accepted terms with appropriate explanations. The list is included in the content of the document.
4.2.3 It is not allowed in the text of the document:
- apply revolutions colloquial speech, technicalisms, professionalisms;
- to apply for the same concept various scientific and technical terms that are close in meaning (synonyms), as well as foreign words and terms in the presence of equivalent words and terms in the Russian language;
- apply arbitrary word formations;
- apply abbreviations of words, except for those established by the rules of Russian spelling, the corresponding state standards, as well as in this document;
- abbreviate the designation of units of physical quantities, if they are used without numbers, with the exception of units of physical quantities in the heads and sides of tables and in the decoding of letter designations included in formulas and figures.
4.2.4 In the text of the document, with the exception of formulas, tables and figures, it is not allowed:
- apply the mathematical minus sign (-) in front of negative values of quantities (the word "minus" should be written);
- use the sign "" to indicate the diameter (the word "diameter" should be written). When specifying the size or maximum deviations of the diameter on the drawings placed in the text of the document, the sign "" should be written in front of the dimensional number;
- use mathematical signs without numerical values, for example> (more),< (меньше), = (равно), (больше или равно), (меньше или равно), (не равно), а также знаки N (номер), % (процент);
- apply indices of standards, specifications and other documents without a registration number.
4.2.5 If the document contains explanatory inscriptions applied directly to the manufactured product (for example, on strips, plates for control elements, etc.), they are highlighted in a font (without quotes), for example ON, OTKL., Or quotes - if the inscription consists of numbers and (or) signs.
Names of commands, modes, signals, etc. in the text should be enclosed in quotation marks, for example "Signal + 27 is on".
4.2.6 The list of allowed word abbreviations is set in GOST 2.316.
If a special system of abbreviations of words or names is adopted in a document, then a list of accepted abbreviations should be given in it, which is placed at the end of the document before the list of terms.
4.2.7 Letter symbols, images or signs must comply with those adopted in the current legislation and state standards. In the text of the document, before the designation of the parameter, its explanation is given, for example, "Ultimate tensile strength".
If it is necessary to use symbols, images or signs that are not established by the current standards, they should be explained in the text or in the list of symbols.
4.2.8 The document should use standardized units of physical quantities, their names and designations in accordance with GOST 8.417.
Along with the SI units, if necessary, the units of previously used systems allowed for use are indicated in parentheses. The use of different systems of designation of physical quantities in one document is not allowed.
4.2.9 In the text of the document, the numerical values of quantities with the designation of units of physical quantities and units of account should be written in numbers, and numbers without designating units of physical quantities and units of account from one to nine - in words.
Examples.
1 Test five pipes, each 5 m long.
2 Select 15 pipes for pressure testing.
4.2.10 Unit physical quantity the same parameter within the same document must be constant. If the text contains a number of numerical values expressed in the same unit of physical quantity, then it is indicated only after the last numerical value, for example, 1.50; 1.75; 2.00 m.
4.2.11 If a range of numerical values of a physical quantity expressed in the same unit of a physical quantity is given in the text of the document, then the designation of the unit of a physical quantity is indicated after the last numerical value of the range.
Examples.
1 From 1 to 5 mm.
2 From 10 to 100 kg.
3 From plus 10 to minus 40 ° С.
4 From plus 10 to plus 40 ° С.
It is unacceptable to separate a unit of physical quantity from a numerical value (transfer them to different lines or pages), except for units of physical quantities placed in tables made by typewritten method.
4.2.12 By giving the largest or smallest values values, the phrase "should be no more (no less)" should be used.
Leading allowable values deviations from the specified norms, requirements, the phrase "should not be more (less)" should be used.
For example, the mass fraction of sodium carbonate in technical soda ash must be at least 99.4%.
4.2.13 The numerical values of the quantities in the text should be indicated with the degree of accuracy that is necessary to ensure the required properties of the product, while the number of decimal places is aligned in the series of quantities.
Rounding of numeric values to the first, second, third, etc. decimal point for various sizes, brands, etc. products of the same name must be the same. For example, if the gradation of the thickness of the hot-rolled steel strip is 0.25 mm, then the entire range of strip thicknesses must be indicated with the same number of decimal places, for example, 1.50; 1.75; 2.00.
4.2.14 Fractional numbers must be given in the form of decimal fractions, with the exception of dimensions in inches, which should be recorded; (but not , ).
If it is impossible to express a numerical value in the form of a decimal fraction, it is allowed to write it in the form of a simple fraction in one line through a slash, for example 5/32; (50A-4C) / (40B + 20).
4.2.15 In the formulas, the symbols established by the relevant state standards should be used. Explanations of the symbols and numerical coefficients included in the formula, if they are not explained earlier in the text, should be given directly under the formula. Explanations of each symbol should be given on a new line in the order in which the symbols are given in the formula. The first line of explanation must begin with the word "where" without a colon after it.
EXAMPLE The density of each sample, kg / m, is calculated by the formula
where is the mass of the sample, kg;
- sample volume, m
Formulas following one after another and not separated by text are separated by commas.
4.2.16 It is allowed to transfer formulas to the next line only on the signs of the operations performed, and the sign at the beginning of the next line is repeated. When transferring a formula to the multiplication sign, use the sign "".
4.2.17 In documents published in a non-typographic way, formulas can be made in typescript, machine methods or in a drawing font with a height of at least 2.5 mm. The use of typewritten and handwritten characters in the same formula is not allowed.
4.2.18 Formulas, with the exception of formulas placed in the appendix, should be numbered with sequential numbering in Arabic numerals, which are written at the level of the formula on the right in parentheses. One formula is designated - (1).
References in the text to ordinal numbers of formulas are given in brackets, for example ... in formula (1).
Formulas placed in annexes must be numbered separately in Arabic numerals within each annex with the addition of an application designation before each digit, for example, formula (B.1).
Numbering of formulas within the section is allowed. In this case, the formula number consists of the section number and the ordinal number of the formula, separated by a dot, for example (3.1).
4.2.19 The order of presentation in documents of mathematical equations is the same as for formulas.
4.2.20 Notes are given in documents if explanations or reference data are needed to the content of text, tables or graphic material.
Notes should not contain requirements.
4.2.21 Notes should be placed immediately after the text, graphic material or in the table to which these notes refer, and typed with capital letters from the paragraph. If there is only one note, then a dash is placed after the word "Note" and the note is also printed with a capital letter. One note is not numbered. Several notes are numbered sequentially in Arabic numerals. A note to the table is placed at the end of the table above the line indicating the end of the table.
4.2.22 In a text document, references to this document, standards, specifications and other documents are allowed, provided that they fully and unambiguously define the relevant requirements and do not cause difficulties in using the document.
References to enterprise standards (STP) and other technical documentation must be stipulated in the product development contract.
Reference should be made to the document as a whole or to its sections and appendices. References to subsections, clauses, tables and illustrations are not allowed, with the exception of subsections, clauses, tables and illustrations of this document.
When referring to standards and specifications, only their designation is indicated, while it is allowed not to indicate the year of their approval, provided that the designation with the year of approval is recorded at the end of the text document under the heading "REFERENCE REFERENCE DOCUMENTS" in the form:
4.3 Decoration of illustrations and applications
4.3.1 The number of illustrations should be sufficient to explain the text presented. Illustrations can be located both in the text of the document (as close as possible to the corresponding parts of the text), and at the end of it. Illustrations must be made in accordance with the requirements of the ESKD and SPDS standards. Illustrations, with the exception of illustrations in the annexes, should be numbered with Arabic numerals sequentially. If there is only one picture, then it is designated "Picture 1".
The illustrations of each application are denoted by separate numbering in Arabic numerals with the addition of the designation of the application before the number. For example - Figure A.3.
It is allowed not to number small illustrations (small figures) placed directly in the text and to which there are no further references.
It is allowed to number illustrations within the section. In this case, the illustration number consists of the section number and the sequential number of the illustration, separated by a period. For example - Figure 1.1.
When referring to illustrations, write "... in accordance with Figure 2" with continuous numbering and "... in accordance with Figure 1.2" with numbering within the section.
Illustrations, if necessary, can have a name and explanatory data (figure text). The word "Figure" and the name are placed after the explanatory data and are positioned as follows: Figure 1 - Details of the device.
(Modified edition, Amendment N 1).
4.3.2 If the text of the document contains an illustration that shows the component parts of the product, then this illustration should indicate the item numbers of these component parts within this illustration, which are arranged in ascending order, with the exception of repeating positions, and for electrical and radio elements - the reference designations established in the diagrams of this product.
The exception is electrical and radio elements, which are adjustment or adjustment elements, for which (in addition to the position number), the purpose of each adjustment and adjustment, reference designation and inscriptions on the corresponding strip or panel are additionally indicated in the figure text.
It is allowed, if necessary, to keep the number assigned to the component part of the product in the illustration within the document.
For layouts of structural elements and architectural and construction drawings of buildings (structures) indicate the brands of elements.
When referring to individual elements of parts (holes, grooves, grooves, beads, etc.) in the text, they are designated by capital letters of the Russian alphabet.
The indicated data are applied in illustrations in accordance with GOST 2.109.
4.3.3 On the information provided in the document electrical diagrams next to each element, indicate its reference designation, established by the relevant standards, and, if necessary, the nominal value of the quantity.
4.3.4 Material supplementing the text of the document may be placed in annexes. Applications can be, for example, graphic material, large-format tables, calculations, descriptions of equipment and devices, descriptions of algorithms and programs of problems solved on a computer, etc.
The appendix is drawn up as a continuation of this document on its subsequent sheets or issued as an independent document.
4.3.5 Applications can be mandatory and informational.
Information applications can be of a recommended or reference nature.
4.3.6 References should be made to all annexes in the text of the document. The degree of obligatory attachments is not indicated when making links. Appendices are arranged in the order of references to them in the text of the document, with the exception of the informational appendix "Bibliography", which is the latter.
4.3.7 Each appendix should start on a new page with the word "Appendix" and its designation indicated at the top in the middle of the page, and below it, in brackets, for a mandatory appendix write the word "mandatory", and for informational - "recommended" or "reference".
The application must have a title, which is written symmetrically relative to the capitalized text on a separate line.
4.3.8 Applications indicate in capital letters of the Russian alphabet, starting with A, with the exception of the letters E, Z, Y, O, H, L, Y, b. The word "Application" is followed by a letter indicating its sequence.
It is allowed to designate applications with letters of the Latin alphabet, with the exception of letters I and O.
When full use letters of the Russian and Latin alphabets are allowed to designate applications with Arabic numerals.
If a document has one annex, it is referred to as "Appendix A".
4.3.9 Applications, as a rule, are performed on A4 sheets. It is allowed to draw up applications on sheets of A3, A43, A44, A2 and A1 in accordance with GOST 2.301.
4.3.10 The text of each appendix, if necessary, can be divided into sections, subsections, clauses, subclauses, which are numbered within each appendix. The number is preceded by the designation of this application.
Applications should be in common with the rest of the document end-to-end numbering pages.
4.3.11 All attachments should be listed in the content of the document (if any), indicating their numbers and titles.
4.3.12 Applications issued in the form of an independent document are drawn up according to general rules- the first sheet with the main inscription according to form 2, subsequent sheets - according to form 2a according to GOST 2.104, GOST 21.101.
If necessary, such an application may have "Content".
4.3.13 Applications or books issued in the form of an independent document, the designation is assigned as part of the document, indicating their serial number in the document code. If an appendix or book has a title page, then the word "Appendix" and its designation in the case of two or more appendices, for example "Appendix B" or "Book" and its serial number, for example "Book 6", are indicated on it under the name of the document.
4.3.14 * It is allowed to use other independently issued design documents (dimensional drawings, diagrams, etc.) as an attachment to the document.
The document, including the document to which the appendices are issued, are assembled into an album with the compilation of an inventory of the album. Inventories assign the designation of the product for which the main document has been developed, and the OP code.
The inventory is compiled in the form 8 and 8a GOST 2.106. First, a document is written into it, for which other design documents are applied as an application. Further, the documents are recorded in the order of their collection in the album. If necessary, a title page is compiled to the album of documents.
_______________
* See "Notes" label. - Note from the manufacturer of the database.
4.4 Building tables
4.4.1 Tables are used for better clarity and ease of comparison of indicators. The name of the table, if any, should reflect its content, be precise and concise. The title should be placed above the table.
When transferring a part of a table to the same or other pages, the title is placed only above the first part of the table.
Digital material is usually tabulated in accordance with Figure 1.
Picture 1
4.4.2 Tables, with the exception of annex tables, should be numbered with Arabic numerals sequentially.
The tables of each annex are designated by separate numbering in Arabic numerals with the addition of the designation of the application before the number. If there is one table in the document, it should be labeled "Table 1" or "Table B.1" if it is shown in Appendix B.
It is allowed to number tables within a section. In this case, the table number consists of the section number and the sequence number of the table, separated by a dot.
4.4.3 All tables in the document must be referenced in the text of the document; when linking, write the word "table" indicating its number.
4.4.4 The headings of the columns and rows of the table should be written with a capital letter, and the subheadings of the columns - with a lowercase letter, if they form one sentence with a heading, or with a capital letter, if they have an independent meaning. At the end of the headings and subheadings of tables, periods are not put. The headings and subheadings of the graph are indicated in the singular.
4.4.5 Tables on the left, right and bottom are usually delimited by lines.
It is not allowed to separate the headings and subheadings of the sidebar and the graph with diagonal lines.
Horizontal and vertical lines delimiting the rows of the table may not be drawn if their absence does not complicate the use of the table.
As a rule, the headings of the graphs are written parallel to the rows of the table. If necessary, the perpendicular arrangement of the headings of the columns is allowed.
The head of the table should be separated by a line from the rest of the table.
The height of the table lines must be at least 8 mm.
4.4.6 The table, depending on its size, is placed under the text in which the link to it is first given, or on the next page, and, if necessary, in the appendix to the document.
It is allowed to place the table along the long side of the document sheet.
4.4.7 If the lines or columns of the table go beyond the format of the page, it is divided into parts, placing one part under another or next to it, while in each part of the table its head and side are repeated. When dividing a table into parts, it is allowed to replace its head or side, respectively, with the number of columns and lines. In this case, the columns and (or) lines of the first part of the table are numbered in Arabic numerals.
The word "Table" is indicated once to the left above the first part of the table, the words "Continuation of the table" are written above the other parts, indicating the number (designation) of the table in accordance with Figure 2. When preparing text documents using software, the inscription "Continuation of the table" is not allowed indicate.
Picture 2
If at the end of the page the table is interrupted and its continuation will be on the next page, it is allowed not to draw the lower horizontal line delimiting the table in the first part of the table.
Tables with a small number of columns can be divided into parts and placed one part next to another on one page, while repeating the head of the table in accordance with Figure 3. It is recommended to separate parts of the table with a double line or a line 2 thick.
Figure 3
(Modified edition, Amendment N 1).
4.4.8 The column "Number in order" is not allowed to be included in the table. The numbering of table columns with Arabic numerals is allowed in cases where the text of the document contains references to them, when dividing the table into parts, as well as when transferring part of the table to the next page in accordance with Figure 4.
Figure 4
If necessary, the numbering of indicators, parameters or other data, serial numbers should be indicated in the first column (sidebar) of the table immediately before their names in accordance with Figure 5. Before the numerical values of quantities and the designation of types, brands, etc. serial numbers are not affixed.
Figure 5
4.4.9 If all the indicators given in the columns of the table are expressed in the same unit of physical quantity, then its designation must be placed above the table on the right, and when dividing the table into parts, above each of its parts in accordance with Figure 2.
If most of the columns in the table show indicators expressed in the same units of physical quantities (for example, in millimeters, volts), but there are columns with indicators expressed in other units of physical quantities, then the name of the prevailing indicator and its designation should be written above the table physical quantities, for example "Dimensions in millimeters", "Voltage in volts", and in the subheadings of the remaining columns, give the name of the indicators and (or) designations of other units of physical quantities in accordance with Figure 4.
To shorten the text of headings and subheadings, graphs of individual concepts are replaced with letter designations established by GOST 2.321, or other designations if they are explained in the text or shown in illustrations, for example - diameter, - height, - length.
Indicators with the same letter designation are grouped sequentially in ascending order of indices in accordance with Figure 4.
4.4.10 The limiting words "more", "not more", "less", "not less", etc. should be placed in one line or column of the table with the name of the corresponding indicator after the designation of its unit of physical quantity, if they refer to the whole line or graph. In this case, after the name of the indicator, a comma is placed before the restrictive words in accordance with Figures 4 and 5.
4.4.11 The designation of a physical quantity unit common to all data in a line should be indicated after its name in accordance with Figure 5. It is allowed, if necessary, to place the designation of a physical quantity unit in a separate line (column).
4.4.12 If the values of the same physical quantity are placed in the column of the table, then the designation of the unit of the physical quantity is indicated in the heading (subheading) of this column in accordance with Figure 6. Numerical values of quantities that are the same for several lines may be indicated once in accordance with with figures 4 and 6.
Figure 6
If the numerical values of quantities in the columns of the table are expressed in different units of physical quantities, their designations are indicated in the subheading of each column.
The designations given in the headings of the columns of the table should be explained in the text or graphic material of the document.
4.4.13 The designations of flat angle units should be indicated not in the headings of the columns, but in each row of the table, both in the presence of horizontal lines dividing the lines in accordance with Figure 7, and in the absence of horizontal lines in accordance with Figure 8.
Figure 7
Figure 8
4.4.14 Limit deviations related to all numerical values of quantities placed in one column are indicated in the head of the table under the name or designation of the indicator in accordance with Figure 9.
Figure 9
4.4.15 Limit deviations related to several numerical values of quantities or to a certain numerical value of a quantity are indicated in a separate column in accordance with Figure 10.
Figure 10
4.4.16 Text repeated in the lines of the same column and consisting of single words alternating with numbers is replaced with quotation marks in accordance with Figure 11. If the repeated text consists of two or more words, at the first repetition it is replaced with the words "The same ", and then - with quotation marks in accordance with Figure 12. If the previous phrase is part of the next one, then it is allowed to replace it with the words" The same "and add additional information.
Figure 11
Figure 12
If there are horizontal lines, the text must be repeated.
4.4.17 It is not allowed to substitute quotes for numbers repeated in the table, mathematical signs, percent signs and numbers, designation of grades of materials and standard sizes of products, designation of regulatory documents.
4.4.18 In the absence of individual data in the table, a dash (dash) should be inserted in accordance with Figure 11.
4.4.19 When indicating in the tables consecutive intervals of numbers covering all the numbers in the series, they should be written: "From ... to ... incl.", "St. ... to ... incl." according to figure 11.
In the interval covering the numbers of the row, it is allowed to put a dash between the extreme numbers of the row in the table in accordance with Figure 13.
Figure 13
Intervals of numbers in the text are written with the words "from" and "to" (meaning "From ... to ... inclusive"), if a unit of physical quantity or number is indicated after the numbers, represent dimensionless coefficients, or through a hyphen, if numbers represent ordinal numbers.
Examples of
1 ... the layer thickness should be between 0.5 and 20 mm.
27-12 Figure 1-14
4.4.20 In tables, if necessary, stepped bold lines are used to highlight the range attributed to a certain value, combine items into groups and indicate the preferred numerical values of indicators, which are usually located inside the stepped line, or to indicate to which values of the columns and rows certain deviations, in accordance with Figure 14. At the same time, an explanation of these lines should be provided in the text.
Figure 14
4.4.21 The numerical value of the indicator is put down at the level of the last line of the indicator name in accordance with Figure 15.
Figure 15
The value of the indicator, given in the form of text, is recorded at the level of the first line of the indicator name in accordance with Figure 16.
Figure 16
4.4.22 Figures in the columns of the tables should be put down so that the digits of the numbers in the entire column are located one below the other, if they relate to the same indicator. In one column, as a rule, the same number of decimal places must be observed for all values of quantities.
4.4.23 If it is necessary to indicate in the table the preference for the use of certain numerical values of quantities or types (brands, etc.) of products, it is allowed to use conditional marks with an explanation of them in the text of the document.
To highlight the preferred nomenclature or limit the applied numerical values or types (brands, etc.) of products, it is allowed to enclose in brackets those values that are not recommended for use or have a restrictive application, indicating in a note the meaning of the brackets in accordance with Figure 17.
Figure 17
4.4.24 For products weighing up to 100 g, it is allowed to give the mass of a certain number of products, and for products made from different materials, the weight for the base materials can be indicated according to Figures 18-20.
Figure 18
Figure 19
Figure 20
Instead of indicating in the table the mass of products made of different materials, it is allowed to give a reference to the correction factors in a note to the table.
EXAMPLE To determine the masses of screws made of other materials, the masses given in the table must be multiplied by a factor:
- 1,080 - for brass;
- 0.356 - for an aluminum alloy.
4.4.25 If there is a small amount of digital material in a document, it is inappropriate to draw up it in a table, but should be given in text, placing digital data in the form of columns.
Example
Limit deviations of the sizes of profiles of all numbers:
in height | ||||
along the width of the shelf | ||||
by wall thickness | ||||
by shelf thickness | ||||
4.5 Footnotes
4.5.1 If it is necessary to clarify individual data given in the document, then these data should be indicated by superscript footnotes.
Footnotes in the text are placed with paragraph indentation at the end of the page on which they are indicated, and are separated from the text by a short thin horizontal line on the left side, and to the data located in the table, at the end of the table above the line indicating the end of the table.
4.5.2 A footnote mark is placed immediately after the word, number, symbol, sentence to which the explanation is given, and before the text of the explanation.
4.5.3 The footnote mark is executed in Arabic numerals with a parenthesis and placed at the level of the upper edge of the font.
Example - "... printing device ..."
Footnotes are numbered separately for each page.
It is allowed to use asterisks instead of numbers: *. It is not recommended to use more than four stars.
4.6 Examples
4.6.1 Examples may be given when they clarify the document's requirements or make them more concise.
4.6.2 Examples are placed, numbered and executed in the same way as the notes (according to 4.2.21).
5 Requirements for text documents containing text, divided into columns
5.1 Text documents containing text divided into columns, if necessary, are divided into sections and subsections that are not numbered.
5.2 The names of sections and subsections are written in the form of headings in lowercase letters (except for the first uppercase) and underlined.
The location of the headings for the statements is established by the corresponding ESKD and SPDS standards.
One free line should be left below each heading, above - at least one free line.
5.3 Notes to sections, subsections or to the entire document are numbered in accordance with 4.2.21.
5.4 In text documents in paper form with lines, all entries are carried out on each line in one row.
To facilitate making changes:
- keep a record at the bottom of the line field. Records should not merge with lines dividing lines and columns;
- leave free lines between sections and subsections, and in large documents - also inside sections and subsections.
When drawing up documents for prototypes, they additionally provide for free lines for recording documents and other data that can be entered into the documentation.
(Modified edition, Amendment N 1).
5.5 If text is written in several lines in a column of a document, then in subsequent columns the records begin at the level of the first line. If in the following columns the record is placed on one line, then with the typewritten method of execution it is allowed to be placed at the level of the last line.
5.6 For electronic documents, when outputting to paper or a display device using software, deviations are allowed in the forms of execution of tables (sizes of frames, graphs, etc.) and the placement of text (sizes of fields, intervals, etc.), subject to this requirements for the design of text documents.
(Introduced additionally, Rev. N 1).
6 Requirements for the title page and approval sheet
6.1 The title page is the first page of the document. The title page, compiled for the album of documents, is the first page of the inventory of this album.
6.2 An approval sheet (LU) is issued for documents on which, according to the terms of their use, the developer and (or) the customer considers it inappropriate to give the names of organizations, positions and names of the persons who signed these documents.
6.3 LU is issued for one document, for several documents, for an album of documents or a set of documents. It is allowed to issue license plate for a separate part or several parts of the document.
6.4 LU designation consists of the designation of the document to which it belongs, with the addition of the LU code through a hyphen, for example XXXX.XXXXXX.XXXTU-LU.
6.5 If an LU is issued for an album of documents, it is assigned the designation of one of these documents with the addition of the LU code, separated by a hyphen, and is written into the inventory of the album first.
6.6 If an LU is issued for several documents, it is assigned the designation of one of these documents with the addition of the LU code, separated by a hyphen, and recorded in the specification, which includes this document.
6.7 If an MD is issued for a set of documents, it is assigned a specification designation with the addition of an MD code and is written into the specification in the "Documentation" section first.
6.8 When writing the LU into the specification, it is necessary to indicate in the "Note" column - "Reproduce as directed".
Notes (edit)
1 LU is multiplied and sent out if necessary. The need for distribution of copies of the license is determined by the holder of the original license in agreement with the customer.
2 They are not included in the list of operational documents, as well as in the list of documents for the repair of LU.
6.9 The title page and license plate are made on A4 sheets in accordance with GOST 2.301 in the form shown in Figure 21:
field 1 - the name of the department, the system of which includes the organization that developed this document. Filling in the field is optional;
field 2 - on the left side (for technical conditions, operational and repair documents) - the code according to the product classifier (for example, in the Russian Federation they use the code according to the All-Russian classifier of products - OKP - six characters), on the right side - special marks. To be completed only for the title page;
field 3 - on the left - the approval stamp, on the right - the approval stamp, performed in accordance with GOST 6.38, if necessary;
field 4 - the name of the product (in capital letters) and the document on which the title page or LU is drawn up. If the title page is drawn up for documents divided into parts, indicate the part number and its name. For a document album, indicate the album number and the total number of albums, for example:
HORIZONTAL MACHINE
MODEL 2620B
Dimensional Drawings
Total Albums 5
Figure 21 - Layout of the fields of the title page and the approval sheet
field 5 - the words "Approval sheet"; the field is filled only for the license;
field 6 - for the title page - designation of the document (in capital letters), for the album of documents - designation of the inventory of this album; for LU - LU designation;
field 7 - the number of sheets of the license plate. The field is not filled in if the license is executed on one sheet;
field 8 - for the title page: signatures of the developers of the document, carried out in accordance with GOST 6.38. If the document is subject to approval by several officials, then in addition to the signatures specified in field 3, the rest of the signatures are placed on the left side of field 8.
The signatures indicated on the title page title block must not be repeated on the title page and approval sheet.
For LU: on the left - the approval stamp (if necessary), on the right - the signatures of the developers and the normative controller in accordance with GOST 6.38 in the manner established at the developer enterprise.
With a large number of signatures, field 8 is increased by issuing a second sheet. At the same time, on it in the upper right corner indicate: for the title page - "Continuation of the title page", for LU - "Continuation of the approval sheet" and then the name and designation of the document. In this case, at the end of the first sheet indicate: "Continued on the next sheet";
field 9 - columns 19-23 in accordance with GOST 2.104, placed on the field for filing. It is allowed to place field 9 on field 10 in accordance with GOST 2.004;
field 10 - columns 14-18 in accordance with GOST 2.104 (dimensions can be set arbitrarily; lines dividing columns and lines are not applied; the name of the columns is not indicated). The field is filled with lines from bottom to top. The field is filled only for the license.
6.10 In the case of issuance of an LU for several documents, in field 8 below the signatures, indicate the designation of the documents to which this LU applies.
6.11 When one or more documents are approved by the approval sheet, an inscription is made on the title page in the upper left corner for text documents or above the title block for graphic documents:
7 Requirements for paperwork for double-sided copying
7.1 For double-sided copying, the sheets of the document are doubled with a fold line in the middle. The main inscription is given on both halves of each sheet (Figure 22), with the exception of additional columns, which are placed only on the odd page.
Figure 22
7.2 In the main inscriptions, the name of the column "Sheet" is changed to "C.", and the name of the "Sheets" (on the title pages) to "Pages".
7.3 Separate sheets of a document (for example, a title page or sheets with graphic content attachments) are published without filling in the reverse side of the copy; such sheets indicate odd page numbers, and the corresponding even page numbers are not indicated, but included in the total number of pages of the document.
7.4 For documents made by duplex copying, the size and number of sheets are indicated as follows:
- the format is written in the form of a fraction, where the format of double sheets of the document is indicated in the numerator, and the format of copies, for example A3 / A4, in the denominator;
- the number of sheets is also recorded as a fraction: in the numerator - the number of double sheets of the document, and in the denominator - the number of pages, for example, 45 / s. 90.
Appendix A (reference). An example of executing a text document
APPENDIX A
(reference)
Appendix B (reference). An example of filling in field 4 of the title page per book
APPENDIX B
(reference)
(Modified edition, Amendment N 1).
Appendix B (informative). An example of filling out an approval sheet for one document
APPENDIX B
(reference)
(Amendment).
Appendix D (reference). An example of filling out an approval sheet for several documents
APPENDIX D
(reference)
Note - Since 2000, the year is indicated in the date with four digits.
(Modified edition, Amendment N 1).
Appendix D (reference). Example of filling out a title page
APPENDIX E
(reference)
Note - Since 2000, the year is indicated in the date with four digits.
(Amendment).
Appendix E (informative). An example of filling out a cover page with an approval sheet
APPENDIX E
(reference)
Electronic text of the document
prepared by JSC "Kodeks" and verified by:
official publication
Unified system for design documentation.
Key points: Sat. GOSTs. -
M .: Standartinform, 2011
Document revision taking into account
changes and additions prepared
The structure of the thesis (course) work
The structure of the thesis is determined by the logic of scientific research. Usually a thesis consists of an introduction, 2-3 chapters, within which paragraphs, conclusions and a bibliographic list are highlighted. Optionally, it is possible to include a list of sources from which the material for research is taken. All materials that are not vital for understanding the scientific problem being solved are included in the appendix.
Each compositionally highlighted part of a scientific work has its own goals, its own content. The introduction substantiates the relevance of the chosen goal, notes the novelty, defines the goal and objectives of the research, the object and subject of the research, characterizes the research material, describes the research methods and the compositional structure of the work.
The first chapter is of an overview nature, it sets out the history of the issue under consideration. In form, the first chapter is an analytical abstract, which sets out the results of research in the area under consideration, outlines the range of unsolved problems, reveals the theoretical prerequisites for studying the problem.
The second chapter (and subsequent chapters, if any) contains a description of the research process, analyzes the factual material.
In the conclusion, the results of the study are summed up: conclusions are formulated, prospects for further work within the framework of the problem raised are outlined.
The minimum volume of the thesis is 40 pages of text (for term paper - 20 pages), typed in Times New Roman, 14 points in size, 1.5 spacing.
Registration of the thesis (course) work
- Sizes of margins: top and bottom - 20 mm, left - 30 mm, right - 20 mm.
- The headings of the structural parts of the thesis "Contents", "Introduction", "Chapter", "Conclusion", "Bibliographic list", "Appendices" are printed in capital letters in the middle of the lines, using a bold font with a size of 1-2 points larger than the font in the main text. Chapter titles are also printed.
- Section headings are printed in lowercase letters (except for the first uppercase) with paragraph indentation in bold type 1-2 points larger than in the main text.
- Subsection headings are printed with paragraph indentation in lowercase letters (except for the first uppercase) in bold font with the font size of the main text.
- Paragraphs, as a rule, do not have headings. If necessary, the heading of the paragraph is printed with a paragraph indent in bold type with the font size of the main text in fit to the text.
- There is no full stop at the end of the headings of chapters, sections and subsections. If the title consists of two or more sentences, they are separated by period (s). At the end of the paragraph heading, put a period.
- The distance between the heading (except for the paragraph heading) and the text should be 2-3 line spacing. If there is no text between two headings, then the distance between them is set to 1.5-2 line spacing. The distance between the heading and the text that the heading follows can be greater than the distance between the heading and the text to which it refers.
- Every structural part thesis should start with a new sheet.
- Page numbering is given in Arabic numerals. The first page is the title page, which is included in the general page numbering of the thesis. On the title page, the page number is not put; on subsequent pages, the number is put down in the center of the bottom of the sheet without a dot at the end.
- The numbering of chapters, sections, subsections, points, figures, tables, formulas, equations is given in Arabic numerals without the "No." sign.
- The chapter number is placed after the word "Chapter". The sections "Contents", "Introduction", "Conclusion", "Bibliography", "Appendices" do not have numbers.
- Sections are numbered within each chapter. The section number consists of the chapter number and the sequence number of the section, separated by a period, for example: "2.3" (the third section of the second chapter).
- Subsections are numbered within each section. The subsection number consists of the ordinal numbers of the chapter, section, subsection, separated by periods, for example: "1.3.2" (second subsection of the third section of the first chapter).
- Items are numbered in Arabic numerals within each subsection. The item number consists of the serial numbers of the chapter, section, subsection, item, separated by dots, for example: "4.1.3.2" (second item of the third subsection of the first section of the fourth chapter). Point numbers are highlighted in bold.
- The chapter title is printed on a new line following the chapter number. The headings of sections, subsections, paragraphs are given after their numbers, separated by a space. The item may not have a title.
At the end of the numbering of chapters, sections, subsections, paragraphs, as well as their headings, do not put a full stop.
- Illustrations and tables should be placed directly on the page with the text after the paragraph in which they are mentioned for the first time, or separately on the next page. Illustrations and tables are designated respectively by the words "figure" and "table" and are numbered sequentially within each chapter. All tables and illustrations should be referenced in the text of the thesis. The words "figure" "table" in figure captions, tables and links to them are not abbreviated.
- The illustration (table) number should consist of the chapter number and the sequential number of the illustration (table), separated by a dot. For example: "figure 1.2" (second figure of the first chapter), "table 2.5" (fifth table of the second chapter). If in the chapters of the thesis only one illustration (table) is given, then they are numbered sequentially within the scope of the thesis as a whole, for example: "Figure 1", "Table 3".
Table decoration
The digital material of the thesis is drawn up in the form of tables. Each table must have a short title, which consists of the word "Table", its serial number and name, separated from the number by a dash. The heading should be placed above the table on the left, without indentation.
When drawing up tables, you must be guided by the following rules:
- it is allowed to use a font 1-2 points smaller in the table than in the thesis text (term paper);
- the column "Number in order" should not be included in the table. If it is necessary to number the indicators included in the table, serial numbers are indicated in the side of the table immediately before their name;
- a table with a large number of lines can be transferred to the next sheet. When transferring a part of the table to another sheet, its title is indicated once above the first part, on the left above other parts they write the word "Continuation". If there are several tables in the thesis, then after the word "Continuation" indicate the number of the table, for example: "Continuation of table 1.2";
- headings of graphs and lines should be written with a capital letter in the singular, and subheadings of a graph - with a lowercase, if they make up one sentence with a heading, and with an uppercase, if they have an independent meaning. It is allowed to number the columns with Arabic numerals, if it is necessary to provide links to them in the text of the thesis;
- graph headers, as a rule, are written parallel to the table rows. If necessary, it is allowed to arrange the headings of the columns parallel to the columns of the table;
- the head of the table is separated by a line from the rest of the table. On the left, right and bottom, the table is also delimited by lines. Horizontal and vertical lines delimiting the rows and columns of the table may not be drawn if it does not make it difficult to read the table;
- it is not allowed to separate the headings and subheadings of the sidebar and the graph with diagonal lines;
- if the table is interrupted and a part of it is transferred to the next page, at the end of the first part of the table, the lower boundary line is not drawn.
Making references to sources, materials or individual results mentioned in the work
- When using information from a source with a large number of pages, you need to indicate in the place of the thesis where the link to this source is given, the numbers of pages, illustrations, tables, formulas, equations to which the link is given. For example: "" (here 14 is the number of the source in the bibliographic list, 26 is the page number, 2 is the table number).
- References to sources in the text of the thesis are carried out by bringing the number in accordance with the bibliographic list. The source number in the list is enclosed in square brackets or placed between two forward slashes.
- Information about the sources used in the thesis is given in the "Bibliography" section. They are formed in alphabetical order of the names of the first authors and (or) titles. Information about sources is numbered in Arabic numerals, printed with paragraph indentation, after the number, a full stop is not put. The content of the information about the sources should correspond to the examples below.
See also Guenon:
Section design "Appendix"
- Section "Appendices", if necessary, draw up at the end of the thesis.
- It is not allowed to include in the application materials that are not referenced in the text of the thesis (term paper).
- Each appendix should start on a new sheet with the word "APPENDIX" in capital letters in the upper right corner.
- The application should have a meaningful title, which is placed on a new line in the center of the sheet with a capital letter.
A course project (course work) is another research work, which is drawn up according to the standard rules of GOST. Of course, sometimes a specific university makes its own adjustments, but this is due to the peculiarities of the discipline being studied. In order for students to know all the rules for the design of various verification and other works, they are given manuals that include all the nuances of the design of theoretical and practical assignments. Curators or teachers, under whose guidance it is, have the right to make changes in the design of a specific work.
What is the "Appendix" to the course work?
This is the final part of the work, which is placed after in a special section "Appendices" or "Appendix". This section is included in the general section without fail — Those students who, for various reasons, neglect the design of this section, lose the main advantage in the eyes of the curator - the opportunity to show themselves as a researcher.
Application examples: 
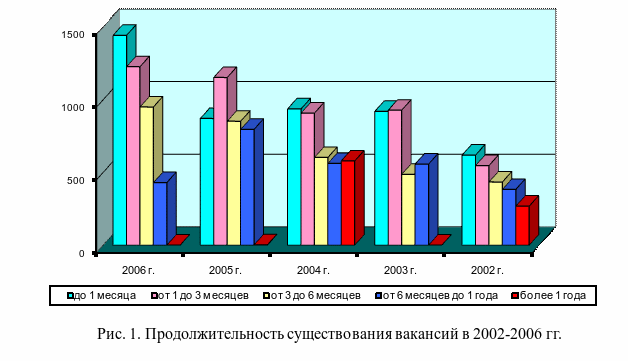
If you are unsure of your knowledge of how to arrange attachments for term paper, you can always turn to our website for help no matter what city you live in, at least, at least, at least in any other.
As a rule, large amounts of information are transferred into applications, based on which certain grounds for work are made. These can be tabular materials, excerpts from monographs by famous authors, graphics, necessary photographic materials, various engineering surveys, etc. A significant number of applications show the teacher how much literature the student studied while preparing his term paper. However, the student should be aware that applications are not counted in a given volume of coursework, although the presence of an application is taken into account when evaluating the work. The types of applications are informational and mandatory, necessary or explaining the main content of the practical part of the work.
How to make an application for a term paper? 
- If there is only one application, it does not need to be numbered.
- If there are several appendices, they are located after the literature squeak in the order as mentioned in the text in the form of footnotes.
- The new application is located on new page! You cannot print two applications on one sheet. If the text of the appendix on one sheet does not fit, the second sheet should have the title "continuation of the appendix No. ..."
- The title "Application" is located in the upper right corner of the sheet. The text of the "attachment" is written in the same font as the entire work. Letter sizes can be larger, italicized, or bold.
- All applications are numbered, and the text should contain links to this application
- Appendix pages are not numbered along with all the text, but they have their own numbering within the "Appendices" section. Instead of numbering, letters of the Russian alphabet can be used without rarely used letters (d, h, h, b, b, s, e)
- In the case when the volume of the appendix is large, it can be divided into chapters and sub-clauses, which are numbered in Arabic numerals depending on the number of the appendix.