Download lesson plans for computer science lessons. Educational-methodical support and lesson software. start MS Word, exit, save the created document, use text editing operations
Outline lesson outline using the project method.
Topic: "Graphic editor".
Class: Grade 5.
Lesson objectives:
- reproduces the concepts of multimedia technology and multimedia presentation, computer graphics.
Defines the types of computer graphics.
- works in a group
Lesson Objectives:
Educational: generalize knowledge on the topic "Graphic editor» .
Developing: develop the ability to analyze, highlight the main thing, develop the creative activity of students, cognitive interest, develop information and communication competence.
Educational: to develop the ability to work in groups and interact well with classmates.
Lesson type: Lesson in the practical application of knowledge.
Lesson type: lesson using the project method.
Equipment: computers, multimedia projector, cards with key phrases for compiling a mini-report.
Lesson plan:
1. Organizational moment.
2. Preparing students for the assimilation of the material (active goal-reading).
3.Practical part(creating projects.):
Students are divided into groups.
Each team is assigned roles: historian, editor, artist.
Project creation.
Protection of projects.
4. Reflection.
5. Summing up the results of the lesson.
During the classes.
Organizing time:
Good afternoon guys! Today we will devote our lesson to the repetition of the topic "Graphic editor". After this lesson, you guys will create projects that you will then present to the audience. You will present your projects in the form of presentations that will contain information about the types of computer graphics.
The whole group will be divided into three teams. Each team will create a project dedicated to its own type of computer graphics. You will search for information on the Internet, but using only certain web resources.
Preparing students to master the material:
You will be creating your project using multimedia presentation means, so you need to remember, what is multimedia technology, and in particular multimedia presentation?
Multimedia technology Is the interaction of visual and audio effects under the control of interactive software using modern hardware and software, they combine text, sound, graphics, photos, video in one digital representation.
Multimedia presentations - These are electronic presentations that consist of separate parts, slides, and can contain texts, video, audio, images, photographs, diagrams, etc. in their structure. Typically, multimedia presentations are used to visually present information to a specific circle of people using hardware and software. Multimedia presentations are created using MS PowerPoint, in our case we will use MS PowerPoint 2007.
Since the topic of the project is computer graphics, it means you need to remember what it is and what types of computer graphicsexist.
Computer graphics Is an area of \u200b\u200bactivity in which used as a tool, how to create and for processing derived from the real world.
Types of computer graphics: raster - images consisting from pixels;vector - images that consist of the simplest geometric shapes;fractal - images created using programming languages. It is based on the principle of repetition of individual parts that add up to a single whole;three-dimensional - images that have a visual volume and can be written in three-dimensional space.
Practical part of the lesson (creating projects):
Now that we have remembered what computer graphics, types of computer graphics, multimedia technologies and presentations are, it's time to start creating projects. To do this, you split into three teams. Each team creates a project according to its own type of computer graphics:
1 team carries out a raster graphics project;
2 team carries out a vector graphics project;
Team 3 carries out the project in 3D.
Assign roles to each team member. You must havehistorian , which will search for information on the network using certain web resources;editor , who, receiving information from the historian, company it and draws up the finished presentation;artist , which creates a rough image of his team's graphics look.
During the creation process, you will use the project creation guide ( ). The manual pit is spelled out in detail what questions need to be disclosed within the framework of the topic of your project.
Now that we have discussed everything for now, proceed to the direct implementation of projects. I ask the teams to go behind the computers (students sit down at the computers). On the desktops of your computers, find a text document namedManual link.txt ... Open this document and copy the link from it. Then close the document and open the Mozilla Firefox browser, which is located on the Desktop. In the address bar of your browser, paste the link to the manual and press the "Enter" key. You are now on the main page of the manual. Carefully read the assignment for each team member, with the questions that need to be disclosed in the project, with the requirements for the design of the project, with a list information resourceswhich you can use when creating projects.
After your projects are ready, each team prepares a mini-report on their project. As a template, you have a list of key phrases that can be used in the report (learners get acquainted with the manual, ask the teacher questions, start projects).
Protection of projects:
Team projects are ready. Now your task is, using key phrases, to compose a mini-report on your projects, in other words, to protect them in front of an audience. You have printouts on your desks with these key phrases. You have 7 minutes to write a report (the students start writing reports).
Basic phrases for compiling a mini-reportOur team carried out a project on the topic ________________________________________.
In the group, the HISTORIAN was ___________________________, the EDITOR was ______________________________ and the ARTIST was _________________________.
Within the framework of this topic, we examined the following issues:
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
After processing the information found, we found out that ____________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________.
Working on the project under the theme ________________________________________, we discovered new facts that were not known to us until now: __________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________.
In the process of creating a project, we used the following methods of working with information(Underline whatever applicable) : search, analysis, synthesis, highlighting the main thing, generalization, analogy, comparison, classification, systematization.
The following image was created by the ARTIST of our team in _________________ editor _____________________. This editor is for ________________________________________________________________ images.
Thank you for your attention!
The reports have been drawn up. It's time to present your projects to the public. We invite the first team to present their project (the teams take turns showing the created projects to the audience and reading reports on them).
Reflection:
All teams did a very good job and prepared wonderful projects on their topics. And at the end of our lesson, I would like to hear from each team their opinion on the projects of their opponents (what they liked, what they didn’t like, what should be improved, etc.) (students express their opinion about the projects of each team).
Lesson summary. Closing remarks from the teacher:
Our lesson has come to an end. I hope you enjoyed working in groups, creating projects and interacting with each other. I think that this experience will not be in vain for you. Thank you all for your active work, our lesson is over. Goodbye!
Outline plan
informatics lesson
« Information Technology
work with text.
Document Editing "
Compiled by: Chudutova Elena Burchievna,
teacher of informatics MBOU "Elista Lyceum"
Elista, 2015
Lesson topic: “Information technologies for working with text. Document Editing ".
Lesson type: learning new material.
The purpose of the lesson:
Educational:
formation of students' knowledge about the purpose and basic capabilities of a text editorMicrosoft Word, familiarization with the structure of the MS Word window, familiarization with text editing operations;
Developing:
development of attention, memory, logical thinking, independence;
Educational:
education of information culture, discipline, perseverance, self-confidence.
Requirements for the knowledge and skills of students:
Students should
know:
purpose and basic features of a text editorMS Word, MS Word window structure.
Students should be able to:
run the programMS Word, shut down, save the created document, use text editing operations.
Educational and methodological support and software lesson:
"Informatics. Basic course. Grade 8 "Semakin IG - Moscow, Laboratory of Basic Knowledge, 2008;
Methodological guide for teachers Semakin I.G. "Teaching basic course informatics in high school ", M .: BINOM. Knowledge laboratory, 2006;
Informatics and ICT. Workshop problem book: in 2 volumes. Vol. 2 / L.А. Pledge, etc .; ed. I.G. Semakin, E.K. Henner. M .: BINOM. Knowledge laboratory, 2011
Lesson equipment: multimedia projector, testing system,MSWord.
Lesson plan:
Org. moment (3 min)
Setting the goals of the lesson. Knowledge update (4 min)
Learning new material (13 min)
Fixing new material (10 min)
Reflection (7 min)
Lesson summary and homework (3 min)
Technological map of the lesson.
Lesson steps
Teacher activity
Techniques and methods
Student activities
Formation of UUD
Organizational moment (3 min)
Greeting students, checking the readiness of students for the lesson, announcing the topic of the lesson,
declaring lesson stages
Verbal
Visual demonstration
Write down the date and topic of the lesson
Personal: creation of a comfortable health-preserving environment, creation of conditions for obtaining knowledge and skills.
Setting the goals of the lesson.
Knowledge update (4 min)
Declaring the objectives of the lesson.
Consolidation of the studied material
(Attachment 1)
Verbal
Visual demonstration
Listen to the teacher
Answer questions
Communicative: mastery of the forms of oral speech
Learning new material (13 min)
Explanation of the new material
(Appendix 2)
Verbal
Visual demonstration
Listen to the teacher
Work with a text editor
Personal: creating conditions for self-knowledge
Regulatory: the ability to formulate your own learning goals
Cognitive: ability to work with instructions
Communicative: understanding the principles of building an interface, working with dialog boxes, mastering style techniques for text design
Securing new material (10 min)
Announcement of exercise numbers to practice editing skills
(Appendix 3)
Problem-search
Exercises in a text editor
Personal:creating conditions for self-realization, the ability to organize your working time
Regulatory:
Cognitive:the ability to plan, analyze, reflect, self-assess their activities, the ability to evaluate the initial data and the planned result, the ability to formalize the results of their activities
Communicative: possession of stylistic techniques for text design
Reflection. (7 minutes)
Organization of work with the test system
(Appendix 4)
Problem-search
Answer questions
Personal: creating conditions for self-realization, creating conditions for acquiring knowledge and skills that go beyond the scope of the taught topic
Regulatory: ability to make decisions, take responsibility
Cognitive: the ability to self-assess their activities, possession of the skills to use technology
Communicative: conducting a dialogue "person" - "technical system", possession of telecommunications to organize communication with remote interlocutors, the ability to work in a group, tolerance, the ability to build communication with representatives of other views
Summing up the lesson. Homework (3 min)
Analysis of students' activities, summing up the lesson, commenting on homework
(Appendix 5)
Verbal
Listening to teachers, asking questions, writing down homework
Regulatory:the ability to set personal goals, understand and realize the meaning of their activities
Cognitive: creating a holistic picture of the world based on our own experience
Attachment 1
How is the text stored on external media? (Text on external media is saved as files)
How many bytes of memory does the binary code of each character take in computer text? (The binary code of each character in computer text takes up 1 byte of memory)
How is each character encoded in the text? (Each character in the text is encoded in an eight-bit binary)
How powerful is the alphabet used to represent texts in a computer? (A 256-character alphabet is used to represent texts in a computer)
What is called an encoding table? (The table in which all the characters of the computer alphabet are assigned serial numbers is called the encoding table).
What is the international standard code? (The international standard is ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange)
What is the rule for the encoding table? (Principle of sequential coding of alphabets)
What is this principle? (Latin letters (lowercase and uppercase) are in alphabetical order, and the arrangement of numbers is in ascending order)
Appendix 2
Teacher: Let's talk about a time when there were no printed books. Is that possible? - you will be surprised. Maybe!
Long ago, books were written by hand. The ancient chronicler sat over books for a very long time, drawing intricate letters. It is incredibly difficult to write an entire book by hand, which is why in ancient times books were considered the greatest value. Sometimes the chronicler worked for many months and years.
Why did the ancient people work for a long time on the creation of the book?
Pupil: written by hand
Teacher: Later people started printing books. In Russia, the pioneer of the printing business was Ivan Fedorov. On April 19, 1563, Fedorov opened in Moscow the first "printing house" in Russia, that is, a printing house. The first book was published for almost a year. Tell me, if Ivan Fyodorov lived in our time, what would help him create a book faster?
Pupil: Of course the computer.
Teacher: Yes, the computer is the main tool for preparing texts.
What types of information does the book contain?
Pupil : text, graphic, numeric.
Teacher: Text editor - an application program that allows you to create text documents, edit them, view the contents of the document, print the document, change the format, etc.
A text document is a file created with a text editor. It consists only of character encoding table codes. Text Document must have a specific structure. It should be divided into lines, paragraphs, pages, sections. Each line ends with special "carriage return" control codes (codeASCII - 13) and "New line" (codeASCII - ten). Often in names text files use the extension.txt - text. There are simple text editors like Notepad and powerful word processors likeMSWORD.
Students sit down at computers. Follow the instructions of the teacher.
In order to start MS Word, you need to do the following:
Start - All Programs -MicrosoftOffice - MS Word or launch MS Word shortcut on your desktop.
Let's take a look at the word processor window. It looks like this:
After starting, the main window of the MS Word editor opens. Let's get acquainted with its elements. On the screen you see the main program window.
The main window can be divided into five main areas:
Title bar
Main menu bar
Toolbar
Workspace
Status bar
Title bar
The title of the window contains the name of the program (Microsoft Word) and the name of the document (by default, Document 1). After the document is saved, the file name appears in the title bar. Files created in Word are automatically assigned the .doc or.docx... On the right side of the title bar are the usual window control buttons (Minimize, Maximize, Close). On the left side of the line, there is a quick access panel, where you can add frequently used tools.
Main menu bar
As with other Windows applications, the Word menu bar is a control that provides access to all the functionality of a program. Each menu item has its own toolbar.
Toolbar
In MS Word 2010, the toolbar opens when you select a specific item in the main menu. The toolbar of each menu item is divided into sections.
Status bar
The status bar is located at the bottom of the main window. The left side of the status bar displays information about the current document:
In addition, the status bar contains operation mode indicators that inform you in which mode you are currently working. The black color of the indicator corresponds to the on state, gray - off. Also on the right side is the Scale tool.
Workspace
The working area of \u200b\u200bthe Word window is the field of the document. In an empty work area, the text cursor representing the character input position is positioned at the first position of the first line. The size of the text on the screen depends on the selected scale. You can set the desired scale using the menu (View -\u003e Scale) or the Scale button in the status bar. In the drop-down list of the Scale buttons select the required value. If the desired scale is not in the list (for example, 90%), the value is entered directly into the text field (the "%" sign can be omitted, it is enough to enter numbers) and press the Enter key.
Rulers
The rulers (horizontal and vertical) allow you to visually estimate the current position of the cursor in the text. However, in MS Word, rulers perform additional, possibly more important functions.
Horizontal ruler allows you to visually change:
Indent paragraphs
Fields per page
Width of columns and columns of tables
Set with mouse tab stops
As you move the cursor, the indentation and tab stops on the horizontal ruler reflect the settings for the paragraph the cursor is in.
Vertical ruler is displayed along the left margin of the page.
With it, you can quickly adjust the top and bottom margins of the page, as well as the height of the rows in the table.
You can display the rulers on the screen as you like, or remove them to free up more space for your document.
Quit MS Word
After completing the current session, you need to exit MS Word. To do this, you can use one of the following methods (slide 14):
Select the File menu -\u003e Exit.
Select the Close item in the system menu of the main MS Word window.
Place the mouse pointer on the system menu icon in the main MS Word window and double-click the left mouse button.
Click the Close button in the title bar of the main window.
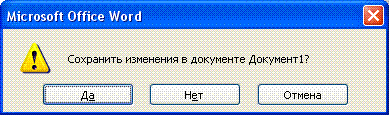
Press Alt + F4 on your keyboard.
If any of the open windows contains unsaved information, MS Word will offer to choose what to do with it. To do this, a dialog box similar to the following will appear on the screen.
To continue the operation, select one of the options
Yes - Saves the document and exits MS Word.
If the file has not yet been named, MS Word will open the Save Document dialog box
No - Exits MS Word without saving the document
Cancel - Closes the current dialog box and returns to MS Word
Working with text editors. Editing.
The skills of entering and editing text are necessary for the user not only to work with a text editor. These skills are basic when working with any type of software that uses interactive mode. With any variant of symbolic input, the user is given the opportunity to correct errors, that is, edit the text. There is a concept of a basic editing standard. It is a set of operations that perform the same for all types of character input.
Basic Editing Standard Techniques:
Appendix 3
Performing exercises No. 1, 6, 7, 9, 10 pp. 9 - 10, p. 5.1 Work with the text from v.2 of the practical book.
Appendix 4
Text Editor test created on a test systemSmartNotebook
Appendix 5
Homework: §14 - 15, questions at the end of paragraphs, exercise. 2, 3, 11, 12
Pavlodar teacher training college them. B. Akhmetova
I approve
Deputy Director for SD
_________ E.A. Poberezhnikova
"___" __________ 20__
Public lesson
on the topic: " Work with theMS Excel»
thing: Computer technology
group: DV-22
teacher: Saganaeva R.S.
The date: 02/14/2015
Lesson topic: Working with MS Excel
Lesson objectives:
educational - acquaint with spreadsheets in the application environment Microsoft Excel; form the initial skill of entering text, numbers, formulas into a cell; give an idea of \u200b\u200bbuilt-in functions; practical application of the studied material; consolidation of knowledge general principles the work of the MS EXCEL spreadsheet processor and the ability to draw up a table for solving a specific problem; Formation of an understanding of calculations in spreadsheets as an important, useful and widely used structure in practice.
developing - to promote the development of logical thinking, memory, attention, creative imagination, the development of the ability to apply educational information in non-standard situations, the development of cognitive interest; development of skills for individual and group practical work; development of skills to apply knowledge to solve problems of various kinds using spreadsheets.
educational - fostering a creative approach to work, a desire to experiment; development of cognitive interest, education of information culture; vocational guidance and preparation for further self-education for future work activities; education of communicative qualities for rational and productive work.
Lesson type:combined.
Lesson form:conversation, group work, individual work.
Interdisciplinary connections:computer science and mathematics.
Equipmentlesson:
personal computers from operating system Windows 7;
multimedia projector, screen;
microsoft Excel program;
the electronic version of the lesson is a PowerPoint presentation;
handouts (for each student) - workbook, laboratory work.
During the classes:
Organizational stage.
Hello! As you can see, we have many guests today. I want to tell you that I am very worried. I think you are also a little worried. Therefore, I extend my hand to you and ask you to extend your hand to me. Hope you can help me today.
Look at the screen and try to formulate the topic of our lesson.
Slide 1-5. Variety of tables.
Slide 6... The topic of our today's lesson is "Working with Microsoft Excel." Today in the lesson we will get acquainted with the Microsoft Excel application environment and learn how to enter text, formulas and numbers into a cell, perform simple arithmetic calculations.
Look at your desk. Each of you received such a sheet. (Demonworkbook is being stripped).This is a page in a workbook. Here we will take notes throughout the lesson. At the end of the lesson, I will give you marks. Sign your workbooks.
2. Learning new material.
Terms and concepts. Slide 7

Spreadsheet is a program for processing and storing numerical data.
The most common among users is the Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. The document created in the spreadsheet is called working book ... Each book consists of worksheets ... Each sheet consists of 65,536 rows and 256 columns. Rows are numbered with integers, and columns are numbered with letters of the Latin alphabet. At the intersection of a column and a row is - cell .
A cell is the smallest worksheet object at the intersection of a column and a row. Cell name Is the column name and row number. Range Are adjacent cells in a row, column, or rectangular area.
Complete in workbook # 1.
Window structureMicrosoftExcel. Slide number 9
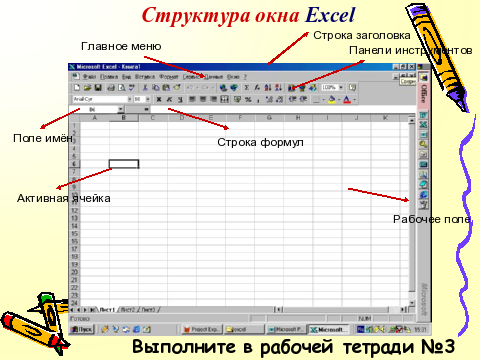
Complete in notebook number 3
Slide number 10.

Active cell -highlighted cell.
Three types of data can be entered into the cells of the worksheet:
numbers (some sequence of characters, which includes numbers and signs "+", "-", or "," (as a separator of integer and fractional parts));
formulas (is a sequence of symbols that starts with the "\u003d" sign);
text (a sequence of characters that is neither a number nor a formula).
Complete in workbook # 5B.
Creation of formulas.Slide number 11
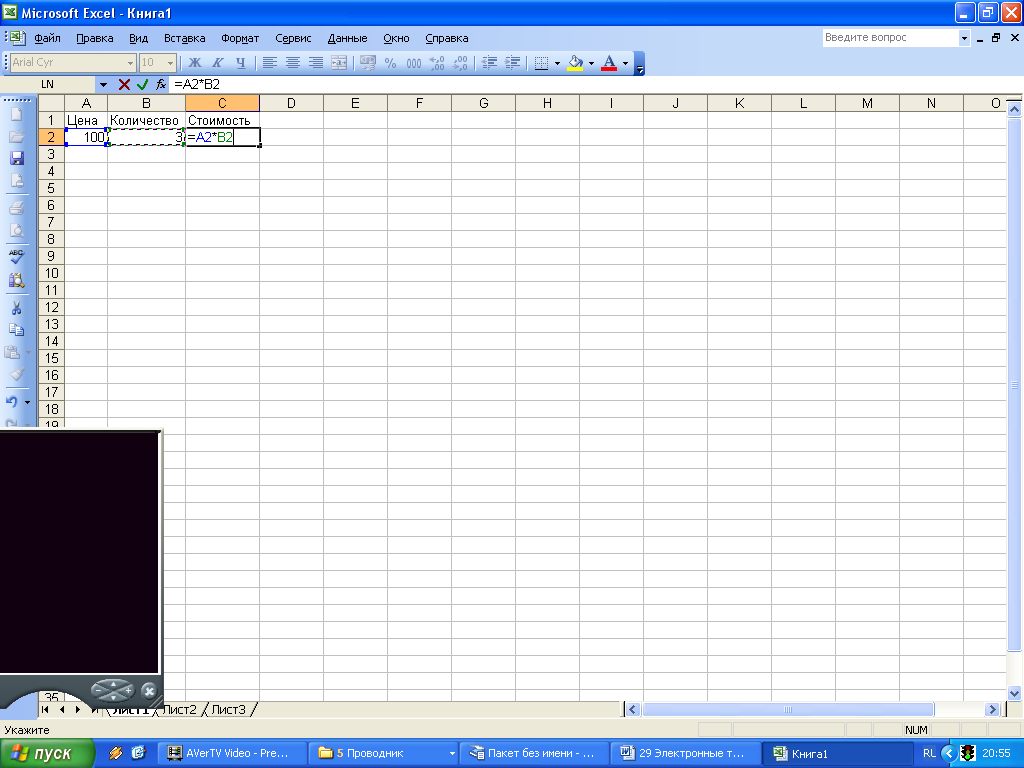
To determine the cost of goods in cell C2, you should go to this cell,
Enter the "\u003d" sign,
Click on the address of cell A2
Put the multiplication sign (*).
Click on the address of cell B2
Entering the formula is completed by pressing the key, after which the result of the calculation appears in the cell.
Complete in workbook # 5A.
Built-in functions in MS Excel are functions that are calculated according to certain algorithms contained in the application.
MS Excel. Slide 14
A call to a built-in function occurs when a formula containing that function is calculated. Slide 15
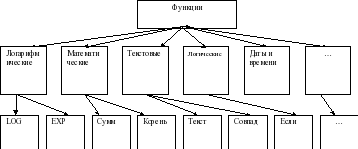
All the many built-in functions of a spreadsheet are divided into several groups: math, statistics, date and time functions, etc.
In different tabular processors the sets of built-in functions vary. Slide 16
Excel contains over 400 built-in functions. The function has a name and a list of arguments in parentheses. Slide 17
Example: \u003d SUM (A4: A7)
Let's take a look at the most commonly used functions.
| Recording type | Appointment |
|
| Mathematical Slide 18 | ROOT(...) | Calculating the square root |
| Calculating the absolute value (modulus) of a number |
||
| Rounds a number or the result of an expression in parentheses to the nearest (!) Integer |
||
| The value of the mathematical constant "PI" (3.1415926 ...) |
||
| Statistical Slide 19 | Determining the minimum of the specified numbers |
|
| Determining the maximum of the specified numbers |
||
| AVERAGE (...) | Determining the average of the specified numbers |
|
| Determining the sum of the specified numbers |
||
| date and time Slide 20 | TODAY () * | Today's date value as a numeric date |
| MONTH (date) | Calculation of the ordinal number of the month in the year by the specified date |
|
| DAY (date) | Calculating the ordinal number of a day in a month by a specified date |
|
| YEAR (date) | Calculating a year from a specified date |
Some commonly used statistics functions can be applied using the icon in the ∑ menu. Complete in workbook # 6.
Securing new material
3 tasks on the board:
1 task: The structure of the MS Excel window (see Appendix 1)
2nd task: Find the correct answers
Special programused to automate the processing of data presented in tabular form is (spreadsheet).
The smallest worksheet object that is at the intersection of a column and a row is (cell)
The cell name is… (column name and row number).
Consecutive cells in a row, column, or rectangular area, this is (range)
The table cell that the cursor is currently occupying is called (active cell)
The cell can fit (text, number, formula).
3 task: Find Correct Formula Entries
Laboratory work:
laboratory work №1 "Creation spreadsheet»,
laboratory work No. 2 "Building a spreadsheet",
laboratory work No. 3 " Built-in functions Excel»
4. Verification work
Test tasks
A spreadsheet is ...
a) a program serving to create, edit, save and print various texts.
b) an application that stores and processes data in rectangular tables.
c) an application serving for the production of calculations and solving mathematical problems.
d) all answers are correct
2.Active cell in Excel is:
a) cell with the A1 address; b) a cell outlined with a frame; c) the cell where the data is entered; d) there is no correct answer
3. Entering the formula in Excel starts:
a) with an equal sign; b) with a parenthesis; c) from a number; d) with a letter.
4. The cell address in Excel consists of:
a) file name;
b) a given set of characters;
c) the name of the column and the line number at the intersection of which the cell is located;
d) row numbers and column names at the intersection of which the cell is located.
5. The SUM () function in Excel refers to the functions:
a) mathematical; b) statistical; c) logical; d) financial.
6. Excel Function Wizard is required for:
a) editing the table; b) to quickly launch the program;
c) preservation of information; d) entering the necessary functions.
7.If you make a cell active in Excel and press the Delete key, then:
a) the contents of the cell will be deleted; b) the cell format will be cleared;
c) the cell will be deleted; d) the cell name will be deleted.
8.Information in the table is presented in the form:
a) files; b) records; c) text, numbers, formulas; d) all answers are correct
Enter the correct cell address:
10.The smallest element in a spreadsheet is ...
a) cell; b) a symbol; c) column; d) string
11.The range of cells in a spreadsheet is called ...
a) the set of all filled table cells;
b) the set of all empty cells;
c) a set of cells that form a rectangular region;
d) a set of cells that form a region of arbitrary shape.
12.Specify an invalid formula for cell F1
a) \u003d A1 + B1 * D1; b) \u003d A1 + B1 / F1; c) \u003d C1; d) all formulas are admissible
13.Specify an invalid formula to write to cell D1
a) \u003d 2A1 + B2; b) \u003d A1 + B2 + C3; c) \u003d A1-C3; d) all formulas are admissible.
14.A group of cells A1: B3 is highlighted in the spreadsheet. How many cells are in this group?
a) 2; b) 3; at 5; d) 6.
15.In a spreadsheet you cannot delete
a) string; b) column; c) cell name; d) cell contents.
5. Reflexive-evaluative stage.
I hope that the work started today will be useful in your future profession.
What did we do with you today? What did you do? What new things have you learned for yourself?
The main advantages of a spreadsheet over a regular spreadsheet are:
is that when the initial data changes, the results are automatically recalculated.
Where can we use ET?
in economic and accounting calculations;
in mathematics;
in physics;
in the study of information models from courses in chemistry, history, biology.
6. Homework: Slide 28
Notebook entries. Design and draw in a notebook the structure of a table for solving the problem using the AVERAGE function.
Today in the lesson you discovered new opportunities for ET, learned how to enter text, a formula and a number into a cell.
Today each of you has risen to a new stage in the development of your thinking. I congratulate you on this event! Thanks to all! The lesson is over.