The wi-fi router has broken. Causes of Wi-Fi router problems
Thanks to a wireless router or router, it is possible to connect the Internet to several computers at once. Also through it you can connect to the Internet using other devices - tablets, mobile phones etc. However, it happens that the router does not work at all or works, but does not provide an Internet connection, and at the very moment when you want to check how, for example, your online children's toys store functions. Failures can be different, and therefore, they will require different solutions.
If the router does not work at all, you need to check its connection to the mains. The contacts may be damaged. Many models have an on / off button, perhaps the problem is with it. Also, a failure may be due to the fact that the power supply burned out. It is not difficult to replace it with a new one. If the problem is not in him and not in the contacts, you will have to carry the router to the service - you will not solve other problems with your own hands.
A completely different question if there is no Internet connection when the router is turned on. First, you need to check the timeliness of payment of the personal account. If everything is in order, the problem may be that the settings are lost after a voltage drop or disconnection of the router from the network. This may be due to the firmware. If such failures are common, you can install a new firmware. To reconfigure the router, you should consult with the provider, since there is no single access configuration scheme for all.

It happens that the router did not have time to establish a connection to the Internet. To check this, you can disconnect it from the network for a couple of seconds, then reconnect it. Be sure to pay attention to the connection settings in your operating system... Perhaps your local network connection is just turned off. Firewall or antivirus can also be a problem. If after temporarily disabling them everything worked, you need to create exceptions for the connection. Also, access can be blocked by virus programs. In this case, it is necessary to perform a full scan of the computer with an antivirus, or better, several.
To avoid such problems, it is recommended to buy only those routers that the provider advises. You will have fewer failures, since the firmware of the routers is tailored for a specific provider. You can find instructions and configure the router yourself, in extreme cases, using the phone prompts of your provider's call center. And then you will not have any problems in order to check at any time and from any device how your online toy store or any other site functions.
Invaluable experience
The Internet is full of instructions for the repair of any radio equipment. Here, only 90% of them can be replaced with one phrase: "opened-saw swollen capacitors-replaced-works". At the same time, people manage to describe the process on several pages. To be honest, I would be ashamed to even write about such a repair.
Today I want to tell you about the repair of Wi-Fi routers based on the products of the well-known "popular" manufacturer TP-LINK. Most of the information is also valid for Wi-Fi routers from other manufacturers. Why TP-LINK? It just so happened that I got a certain number of faulty routers from this manufacturer from the warranty service of one company. The company is small and going through hard times, so its management found it unprofitable to hire an engineer and repair Wi-Fi routers that customers returned under warranty. Perhaps, from their point of view, they did the right thing. This state of affairs also more than suited me.
For some models of routers, especially ADSL models, the network part, Wi-Fi and telephone circuitry are made on separate microcircuits. Most cheap and popular Ethernet models, for example TL-WR740 (741), 720, 841, 3220, etc. on the board all functions are performed by one microcircuit - the processor. If it is damaged in whole or in part (the WAN and / or LAN port is punctured), and this happens often, the repair of such a router is impractical. The processor is sealed to the board with its base, the contacts on the bottom are small and in two rows. A processor microcircuit costs from 5 to 10 dollars, a fully functional second-hand router is sold for a little more than 10. The fuss of buying and replacing a processor is unprofitable, it is easier to throw such a router away or use it as a donor.
YES, do not forget that if the router came to you from the wrong hands, it must have changed the passwords for Wi-Fi and access to the admin panel. Therefore, before repairing, we will try to reset it to factory settings. I think you know how to do it.
We will carry out troubleshooting and determine what and how we will repair, and what we will not. Let's make a table:
We identify a malfunction if the router starts or starts, but there is no way to go to the admin panel.
| Malfunction (symptom) | Decision |
| 1. No LEDs are on |
The processor does not start for some reason. Possibly a power problem. Checking the external power supply (by replacing), checking the stabilizer on the board, checking the processor temperature (if it is hot after a couple of minutes, the processor died, it makes no sense to revive the patient). Surprisingly, the power supplies for TP-LINK routers, although simple as a rake (on the AP3706 controller, are made according to a typical datasheet scheme), work well and are assembled from high-quality components. Therefore, they are very reliable and fail very rarely. Not comparable to competitor D-LINK PSUs. |
| 2. Only the "network" LED is on |
This malfunction is quite common and ambiguous. Option 1 - the processor starts, but it cannot read something intelligible from the flash memory. For routers from the guarantee, this by 90% means that a smart user, having read articles on the Internet, flashed his router with alternative firmware (Openwrt, DD-WRT, Gargoyle, etc.), then he could not figure it out, he wanted to return his native firmware and for his curvature, he "turned out" the router. Another option is a buggy flash memory chip, which is also easy to check and solve the problem. You can try to flash the router via tftp. The Internet is full of instructions on how to do this. It's easier for me to solder the microcircuit, change it on the programmer, test it and, if necessary, replace it with a new one. The chance that after that the router will work properly is almost 100%. Do not forget that the flash chip stores mac-addresses and wi-Fi password by default, the one written on the back of the router case. On the good, you need to change them in the firmware dump, otherwise it may turn out that devices with the same mac addresses may appear on the same network. And this, you know, is not good ... I have 99% of routers with these symptoms come to life. 2nd option - CPU problem. Either it "dies" or some of the contact pads are soldered off from overheating. I had several cases when, after warming up with a hairdryer and light pressure, the router came to life and subsequently worked without problems. If the processor is at the “dying” stage, only its replacement will help. And this is not at all easy and completely unprofitable. |
| 3. The router turns on, the "network" LED lights up, then after a few seconds all the LEDs light up and the processor restarts (cyclic reboot) |
The flash memory chip has incorrect firmware or "garbage". Everything is the same as in the previous case. Checking the flash chip, flashing the correct dump. I have 100% of routers with such symptoms come to life. |
| 4. The network LEDs and all 4 LAN LEDs are on. The rest are paid off. | The flash microcircuit or its strapping is 100% out of order. I had a case when one of the resistors (jumper) near the flash microcircuit disappeared from the board, was poorly soldered and fell off from vibration (maybe the router fell). Was there any other option when a thin track to one of the legs of a flash memory chip and a "dead" flash drive burst. I have 100% of routers with such symptoms returned to service. |
| 5. "Network" LED and "LAN" LED (one or more) and / or "WAN" are on when cables are not connected, "WiFi". | The processor ports are punctured. An alternative treatment is to cut the tracks from the processor to the matching transformers of the corresponding port. The LEDs will go out, the punctured ports will no longer interfere with the operation of the serviceable ones. In principle, if the LAN port is punctured after that, it is still fully functional with wi-Fi and other ports. If the WAN port is broken, it is worse. Without a WAN port, a router ceases to be a router and can work as just a point wi-Fi access or as an expander Wi-Fi networks by WDS technology. Alternatively, flash an alternative firmware and assign the WAN port to any of the working LAN ports. But in any case, such routers are not of commercial interest, it is almost impossible to sell them. Whether it is worth bothering with them, I do not know. I have a dozen of them lying around. It seems a pity to throw it away ... |
| 6. When the LAN cable is connected, the LED of not only the port to which it is connected, but also the LED of the other LAN port will light up. | The LAN port is broken. An option is to cut the tracks from the processor to the matching transformers of the burnt-out port. After that, the punched port (s) will not interfere with the operation of the router. The rest of the functionality will remain. |
| 7. Other cases. | It is not worth it. Router for release (to organ donors). |
On the board, next to the processor, another microcircuit is soldered random access memory... I do not consider the option of its failure because I have never come across routers with faulty RAM and I do not know how to guarantee to identify its malfunction. Most likely the router will not start. In those cases when the processor did not start, I specifically identified the failure of the processor itself, it very quickly heated up to temperatures above 100 degrees.
Now we will consider the cases when the router is loaded and makes it possible to enter the admin panel.
Option with punched (burnt out) lAN ports we have already covered above. We will not return to them anymore.
We identify a malfunction if the router starts up and it is possible to enter the admin panel.
| Malfunction (symptom) | Decision |
| 1. When the WAN cable is connected, the LED does not light up, or it lights up, but there is no Internet connection and in the admin panel in the WAN section it is written that the WAN cable is not connected. | Open in WAN port circuits. We look at the matching transformer of the WAN port and the resistors near it. I have had several cases of broken transformer or resistors. Theoretically, an inter-turn circuit in a transformer is also possible, but I have not had a single such case. If the transformer and resistors are working, the problem is most likely still in the WAN port of the processor. |
| 2. When the LAN cable is connected, the LED does not light up, or it lights up, but there is no connection to the router. It is impossible to enter the admin panel from this LAN port |
Everything is the same as for the WAN port. We look at the matching transformer of the WAN port and the resistors near it. |
| 3. Periodically the router is overloaded. |
We look at the oscilloscope for power after the stabilizer. replacement of capacitors or microcircuit may be required. Alternatively, we look at the thermal mode of the processor. I have had cases when, after sticking on the processor on top of a small radiator, the router began to work stably. |
| 4. Weak Wi-Fi signal. | There have been cases. First of all, I throw in another antenna from the donor (since there are enough spare parts). In my case, the problem disappeared. If soldering the antenna did not help, you can watch the chain from the antenna to the processor, I never had to. |
| 5. Wi-Fi falls off periodically | In my case, there was a processor issue. Soldered from the donor and it all worked. You can replace the antenna to clear your conscience, although this is unlikely to help. Most likely, there is no point in messing around with such a router. It will be unprofitable. |
Well, now there are some pictures with captions.

This is what a typical router looks like from the inside. In the center - the processor, at the top left - flash, on the right - RAM.

On the left is the processor, to the right is flash memory.

Flash chips from different manufacturers.

That's what's under the processor. The bottom is soldered and the contacts are in 2 rows. Re-soldering such a processor is still a pleasure. No, of course it is possible, but is it worth it?
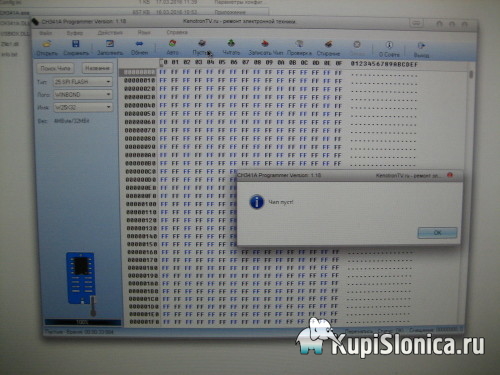
Programmer window after erasing the flash chip and checking it. I'll tell you about the programmer and its software in a separate review, it's worth it.

5dBi antennas in different colors, detachable and not.

Matching transformers. On the left is WAN, on the right are two LANs.

And here, on the contrary, on the right is WAN (next to there is another one that was soldered from the donor), on the left is 1 LAN

This is what's inside the WAN port matching transformer.

Soldering the transformer is easy, but not so easy either. There is a great risk of pulling out the leads and spoiling the transformer or the metallization of the board holes. You need to be careful and not rush. Resistors are visible near the transformer. Very rarely, but it happens that they fail and go into a cliff. It is easy to check them, but not very soldering. They are too small and close to the transformer. But nothing is impossible.

My know-how. I soldered a socket into one test router and now, after soldering the transformer from the donor, I test it. This allows you to be sure that you are soldering a 100% serviceable transformer, without short-circuiting turns. A transformer with short-circuited turns rings as normal, you can check it only by plugging it into a known-good router.

The tested transformer in the socket feels very confident and fits snugly.

And this is how the transformer of 2 LAN ports looks from the inside. By the way, after this execution (trepanation) he remained a worker.

My favorite problem is a dead flash. More precisely, this board does not have it at all.

In the lower left corner there is a built-in Wi-Fi antenna. Strange, but even with it 720 TP-Link is very good. But there is still a place where you can solder a normal external antenna. Then this router generally becomes a beast and gives off the Internet with such force that network cable pulls out of the walls ...
This concludes my small review. I wrote it quickly and somewhat messy. I will warn you that it is designed for more or less trained users. I deliberately do not chew on some points in detail, but simply say what needs to be done, trained people should know how to do it, and it is better for unprepared people not to get into it.
A common situation is when a certain network device, including home router, does not react to anything, and the user decides: it is faulty. How to check if the router is working?
Any of the devices, the router itself or its power supply, can fail. In addition, the router can be configured in a mode in which it is "unavailable" even through ping. How to get around this all in order to understand what is actually faulty - we must consider.
Router and power adapter
The first action you need to perform is factory reset. Without this, trying to define something will be pointless. It is also advisable to get a known working power supply unit compatible with this device before turning it on. If the "Network" light is on, this does not mean that "everything is working" (the adapter voltage, for example, may not be filtered, but the LED will still be on).
The following is the standard sequence of actions: hard reset, configuring the network card, ping.
It is important to know that the use of power adapters not included in the manufacturer's recommended list will void the warranty.
Standard sequence of actions
Resetting previous settings
First of all, you need to find the reset button installed on the router case. She - exists in any case:

Reset button
ASUS has a button called "reset / restore" (reset / restore). If you can find what you need, do the following:
- All signal cables - must be disconnected. Turn on the power supply of the router, wait 1.5 minutes
- The reset button on the router case - press without releasing it for 10-19 seconds (this is important)
- Releasing the button, we get the device with the default settings
In the process of holding the button, the indicators should "blink" or change the combination of the included ones. As soon as this happens, reset is released.
It is important to know that holding reset for more than 20 seconds means putting the device into emergency recovery mode (which is true at least for ASUS routers). Be careful.
When the reset is complete, you can turn off the router itself (to connect the LAN cable to it). So, as discussed above, reset is performed on the vast majority of device models. Except for quite exotic 3Com (find instructions for them).
Configuring a network card
Look for the instructions for the router. It contains the value of the IP address on which it is available. For D-Link DIR-XX it is 192.168.0.1. For many other models - 192.168.1.1.
The router is connected to the computer as follows: any of the 4 LAN ports is connected to a network card (via a patch cord).
Then, configure the computer's network card:
- Go to "Internet Protocol TCP / IP" -\u003e "Properties"
- As the IP address, indicate a value that differs from the router's IP by the last digit (see example)
- Mask - necessarily "with the last 0"
- As a gateway - indicate the router itself (its IP).
The result will look like this:
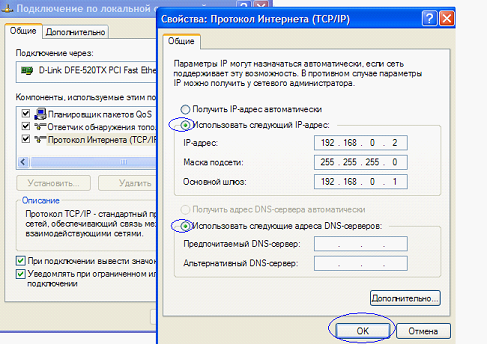
Example of configuring a network card (for D-Link DIR)
After clicking "OK", turn on the power of the router. And wait 1-2 minutes.
We execute the Ping command
Open a command prompt console. This program must be run with administrator rights.
Then, we perform the last action: we type ping "address of the router" Enter. The correct result looks like this:

Ping result
What to check:
- Response time (time) - should be approximately one (and - no more than a few ms)
- If Lost is greater than 0% (but less than 100%) - the router is faulty
- On repeated ping, the result is not too different from the first
Actually, that's all. If ping failed, the device may be in recovery mode. You cannot take it out of this mode, and it is recommended to install the firmware in the SC (we carry the router in service center). Now - exactly, that's it.
How to reset the router (if someone is not very clear) will be shown in the video. Often, though not always, all information is indicated on the label. The value of the IP address can also be found there.

Body sticker
For routers that do not have LAN ports, the steps are the same, but you need to connect to the device via Wi-Fi (by searching for a network 2 minutes after turning on). Then, open a console and ping. Happy settings!
And now - the movie:
A router is used to connect multiple devices, a computer, laptop and others, to the Internet via wired or wireless technology and create a local network between these devices. At the same time, the router implements a barrier between the local network created by it and the Internet. Basically, routers work using NAT - Network Address Translation. Sometimes providers provide routers with the connection, the router can be inside a DSL modem or cable, or purchased separately. But like any electronic device, routers can fail and many malfunctions can be eliminated at home on their own. Consider some common router malfunctions and methods for their elimination, repair of a d link router.
Most often, the following reasons lead to router malfunctions:
- large voltage surges in the network,
- overheating of the router,
- glitches software router (firmware crashes),
- high-frequency interference of electromagnetic radiation during a thunderstorm (in this case, the wan port most often burns out, if the provider does not install lightning protection on its cable),
- human factor.
If the router malfunctions, it can lose data packets, work on the Internet and the local network is disrupted, the firmware gets lost, the router can turn off, all indicators blink.
Solving a malfunction related to the impossibility of entering the settings of the router at its network address 192.168.0.1
If after dialing in the address bar of the router's network address, the router settings page does not open, then to eliminate this malfunction, you should perform the following operations:
- First, check that you have set in the settings of the network card to automatically obtain for the IP address and DNS address (using a direct connection to the router).
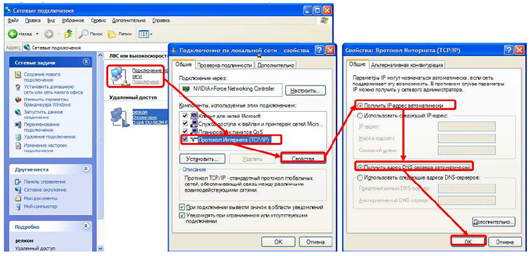
- If the settings of the network card are correct, then you must use the Run command (press the key combination Win + R), then enter - cmd and press enter. Now you need to enter ipconfig on the command line.
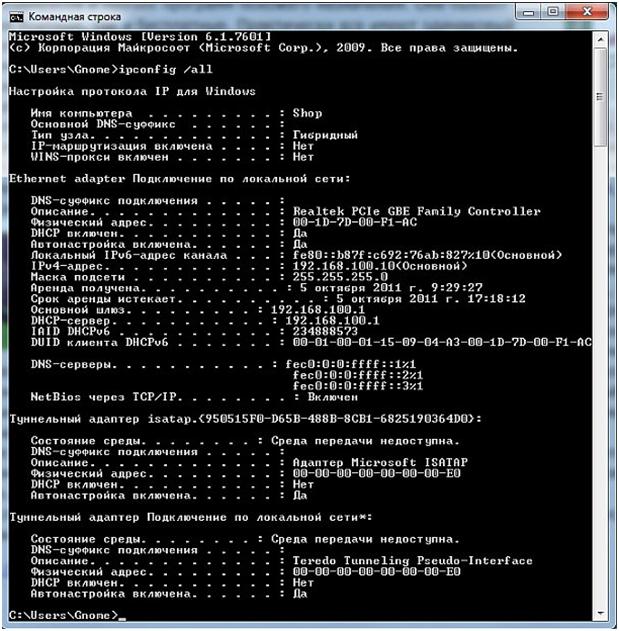
Command line "ipconfig"
In the displayed settings, you need to see what value is opposite the inscription - Main gateway. This address is used to enter the settings of the router. If the value of this address does not match the standard value, then the router may have been configured for a specific network with its own requirements. In this case, you need to reset this value to the factory settings. Sometimes this field may contain no address value at all, and you also need to reset the router. To reset the router, you need to press and hold the Reset button on the router for a while. Usually five or ten seconds are enough. The hole in the button is narrow enough so you can use a ballpoint pen, needle or paper clip to press it.
![]()
If resetting the router does not help, disconnecting the ISP cable from your router may help. Pull out the provider's cable from the router connector and configure the router without a cable connected. After that, you can reconnect the cable to the router.
Also check the firmware version installed in the router. Take a look latest version firmware on the manufacturer's website and update it if necessary. You can also check the drivers of your network card on your computer and reinstall them if necessary.
If the router settings are not saved
To troubleshoot a problem with not saving the router settings or if it is impossible to restore the settings from a separate file, you can try to carry out these operations by opening another browser. This method can help with other router malfunctions.
Computer (laptop, etc.) does not see the WiFi network
There can be many reasons for such a malfunction, and all of them are approximately equally common. Let's consider the main possible causes.
If the network of your router is not displayed on the laptop in the list of available networks, then you need to check that the wireless network module is turned on. This can be done by looking at the adapter settings in the Network Sharing Center on your laptop. The wireless connection must be turned on. In the off state, it will be grayed out and you will need to turn on wireless connection... If you cannot turn it on, then you need to check if your laptop has a Wi-Fi switch and turn it on.
If, despite the fact that the wireless connection remains enabled, but shows the status - No connection, then you should check if the correct drivers are installed for the Wi-Fi adapter and, if necessary, install them. The drivers must be downloaded from the website of the manufacturer of your equipment. This avoids possible problems driver incompatibility.
In addition, you can try to go to the router menu and change the value for the settings there and change the b / g / n parameter to b / g. If this change helps, it means that the 802.11n standard is not supported. You can also see how the channel is specified in the same settings wireless network, and if there is - Automatic, then select a channel from the list.
Other malfunctions
If you have frequent connection breaks during work, it is recommended to update the router firmware. In many cases, this procedure will solve the problem.
Sometimes, when working with some Internet providers, to access local resources (torrent trackers, game servers), you need to configure static routes in the router settings. Such settings can be found on the forums of the provider providing you with the Internet.
Malfunctions of power supplies in routers
Surely, many have already come across the fact that the most weakness many routers are their power supplies. They often break down due to large voltage drops in the power grid and the failure of individual elements as a result of long work.
Defective or low-quality elements, a scheme that is not designed for some margin, can also lead to breakdowns. There are some typical faults of power supplies. In this article, we will consider repairing a power supply for a D-Link router. Power supplies such as JTA0302D-E and the like are used to asus routers and D-Link, designed for an output voltage of 5V and a maximum current of 2-3 A. The appearance of such power supplies can be seen in the figure below.

If we consider the circuit and design of similar power supplies, then this is a diagram of conventional single-ended switching power supplies. In such circuits, a PWM controller is used for control, which controls the operation of a field-effect transistor, which is connected to its output. As a result, the voltage is reduced to the desired value and rectified, and it is supplied to the output. A schematic diagram of such a power supply can be seen in the figure below. In this diagram, depending on the model of the power supply, there may be some minor changes in the ratings of individual components. The power supply delivers a voltage of 5 volts. This voltage should not drop significantly under load (with the router turned on).
To repair the power supply, you may need to use a soldering iron, solder, multimeter, knife and electrical tape. To open the plastic case of the power supply, you need to cut the glued seam of the case. This operation can be done with a knife, but it is more convenient to use a small bur-machine for these purposes.
If you look at the power supply circuit in Fig. 2, you can see that a 2 ampere fuse, a choke, a thermistor and a rectifier bridge of four 1N4007 diodes are installed at the input. If there is a large voltage surge in the network, then all these elements can burn out. They can be easily checked with a multimeter by measuring their resistance. To smooth the rectified output voltage, a capacitor is placed after the diode bridge large capacity - C1 (22 or 33 μF). This capacitor should be 400V, no less. If he is out of order, then this can be determined by his appearance, it swells.
In addition, a positive voltage from the diode bridge is applied to a PWM chip, in this case UC3843B. This microcircuit is used to control the opening and closing of the field-effect transistor P4NK60Z. Often the power circuit of this microcircuit contains a malfunction. This circuit contains an electrolytic capacitor C6 and a zener diode ZD1, which is rated for a voltage of 20 volts. This capacitor must be of a certain capacity so that during operation the voltage supplying the microcircuit is always within the permissible operating limits. Therefore, the recommended capacitance is 100 μF. If the capacitor is dry, then the capacity will not be enough to start the microcircuit,
It is quite difficult to determine by external signs such an inoperative capacitor. Its small size does not allow you to notice some bulge on its lid. You can measure the capacitance of a capacitor, but often with normal capacitance there is a large drop in ESR. To check ESR, special measuring instruments are needed, this cannot be checked with an ordinary multimeter or tester.

In case of voltage drops, the zener diode ZD1 may fail. This can be seen from the darkened (charred) body of the zener diode.
In rare cases, the P4NK60Z field operator may fail. This transistor is supplied with a voltage of 13-15V. from the PWM output. The efficiency of the field-effect transistor can be checked with a multimeter (tester) switched to the diode test mode. On the drain-source channel, the voltage drop is 0.6-0.8 V.
If the voltage at the output of the power supply is 5 V, and when the load is connected, it drops to about 2 V., then most likely the electrolytic capacitors at the output of the power supply (C9 and C11) have dried up. To eliminate this malfunction, it is necessary to replace the dried electrolytic capacitors with working ones with the same characteristics.
In general, the main repair steps can be identified. If there is no voltage at the output of the power supply, then it is necessary to check for breakdown by measuring the resistance F1, TR, rectifier bridge. To provide some starting margin, it is desirable to use the capacitor C6 of 10 μF and rated for 50V, and not 47 μF and 25V. as usual in the diagram.
In cases where the output voltage drops, unstable operation of the power supply is observed, you must first replace the electrolytic capacitors C1, C9, C10, C11.
In addition, you can recommend several recommendations to improve the performance of the power supply. At the output of the power supply, a 220 Ohm 0.125w resistor is usually installed, filled with a special sealant. This resistor operates at its limit values \u200b\u200band therefore gets very hot. Heating causes the condenser C9 to dry out. It is advisable to put a 300 Ohm resistor and a power dissipation of 0.5 W instead of a 220 Ohm resistor. If a capacitor C9 for 10v is installed in the circuit, then it is better to put the same one instead, but designed for 16v.
After repair, the body must be assembled. But you do not need to glue it, but fasten the two halves, for example, with a coupler, so that in the future, if repair is necessary, it can be easily disassembled again.